
最新刊期
卷 44 , 期 6 , 2025
-
 摘要:An efficient computational framework was established to systematically characterize and predict clinical phenotypes of cobalamin C(cblC) deficiency,attempting to disentangle its phenotypic complexity. This framework was based on UHPLC-QE orbitrap MS technology combined with network analysis and chemometrics. UHPLC-QE orbitrap MS-based serum untargeted metabolomic profilings were collected in positive and negative ion modes,separately. Data-driven network algorithm,Connect the Dots(CTD),quickly searched high-connected perturbed metabolites. Chemometric algorithms learned subtle alteration patterns of identified perturbed metabolites between groups. Investigated by two clinical phenotypes(epilepsy and metabolic syndrome),the results showed that perturbed metabolite subset identified by CTD algorithm exhibited high specificity to clinical phenotypes. The perturbation of the involved enriched pathways was reported to be closely correlated with the pathogenesis of epilepsy and metabolic syndrome,separately. For the most significant enriched pathways,epilepsy was associated with the perturbation of sphingolipid metabolism(positive ion mode) and fatty acid biosynthesis(negative ion mode). Metabolic syndrome was associated with the perturbation of arginine and proline metabolism(positive ion mode) and purine metabolism,pyrimidine metabolism,tryptophan metabolism(negative ion mode). Further,CTD algorithm enabled the quantification of covariation information between high-connected perturbed metabolites and construction of main disease modules to systematically characterize complex pathogenic mechanisms of epilepsy and metabolic syndrome,separately. Based on the identified perturbed metabolites,partial least squares discrimination analysis (PLS-DA),support vector machine(SVM) and random forest(RF) achieved desired predictive capabilities using 5-fold cross validation. The averages of area under receiver operating characteristic curve(AUC) were 0.849,0.897 and 0.909 for epilepsy,0.889,0.931 and 0.921 for metabolic syndrome;and of Matthews correlation coefficient(MCC) that were 0.667,0.668 and 0.723 for epilepsy,0.686,0.696 and 0.787 for metabolic syndrome,respectively. All the findings demonstrated the effectiveness of the proposed computational framework in revealing the phenotypic complexity of cblC deficiency and guiding its personalized diagnosis both in positive and negative ion modes.关键词:cobalamin C deficiency;systematic characterization and prediction of clinical phenotypes;UHPLC-QE-Orbitrap MS;CTD network algorithm;chemometric algorithms;personalized diagnosis364|39|0更新时间:2025-06-09
摘要:An efficient computational framework was established to systematically characterize and predict clinical phenotypes of cobalamin C(cblC) deficiency,attempting to disentangle its phenotypic complexity. This framework was based on UHPLC-QE orbitrap MS technology combined with network analysis and chemometrics. UHPLC-QE orbitrap MS-based serum untargeted metabolomic profilings were collected in positive and negative ion modes,separately. Data-driven network algorithm,Connect the Dots(CTD),quickly searched high-connected perturbed metabolites. Chemometric algorithms learned subtle alteration patterns of identified perturbed metabolites between groups. Investigated by two clinical phenotypes(epilepsy and metabolic syndrome),the results showed that perturbed metabolite subset identified by CTD algorithm exhibited high specificity to clinical phenotypes. The perturbation of the involved enriched pathways was reported to be closely correlated with the pathogenesis of epilepsy and metabolic syndrome,separately. For the most significant enriched pathways,epilepsy was associated with the perturbation of sphingolipid metabolism(positive ion mode) and fatty acid biosynthesis(negative ion mode). Metabolic syndrome was associated with the perturbation of arginine and proline metabolism(positive ion mode) and purine metabolism,pyrimidine metabolism,tryptophan metabolism(negative ion mode). Further,CTD algorithm enabled the quantification of covariation information between high-connected perturbed metabolites and construction of main disease modules to systematically characterize complex pathogenic mechanisms of epilepsy and metabolic syndrome,separately. Based on the identified perturbed metabolites,partial least squares discrimination analysis (PLS-DA),support vector machine(SVM) and random forest(RF) achieved desired predictive capabilities using 5-fold cross validation. The averages of area under receiver operating characteristic curve(AUC) were 0.849,0.897 and 0.909 for epilepsy,0.889,0.931 and 0.921 for metabolic syndrome;and of Matthews correlation coefficient(MCC) that were 0.667,0.668 and 0.723 for epilepsy,0.686,0.696 and 0.787 for metabolic syndrome,respectively. All the findings demonstrated the effectiveness of the proposed computational framework in revealing the phenotypic complexity of cblC deficiency and guiding its personalized diagnosis both in positive and negative ion modes.关键词:cobalamin C deficiency;systematic characterization and prediction of clinical phenotypes;UHPLC-QE-Orbitrap MS;CTD network algorithm;chemometric algorithms;personalized diagnosis364|39|0更新时间:2025-06-09 -
 摘要:Epimedium brevicornum and Epimedium pubescens are commonly used traditional Chinese medicines,and their active ingredients such as epimedin A,epimedin B,epimedin C and icariin have important effects on pharmacological effects. In this study,the desktop and portable near-infrared spectral data of Epimedium brevicornum and Epimedium pubescens were collected,and the content data of Epimedin A,Epimedin B,Epimedin C and Icariin were determined by HPLC,and then the partial least squares regression(PLSR) model and support vector regression(SVR) model were established. In order to realize the model adaptation and transfer between desktop near-infrared spectral data and portable near-infrared spectral data,two standard sample set selection methods were explored in the study:hierarchical clustering method and SPXY algorithm,and two model transfer methods were applied:direct correction(DS) method and piecewise direct correction(PDS) method. The results show that the standard sample set selection method and the model transfer method have significant impacts on the model transfer effect. Further verification by paired t test showed that there was no significant difference between the predicted value and the real value of the optimal transfer model (P > 0.05),which indicated that the established transfer model had good adaptability among different instruments. This study provides a basis for the quantitative analysis and model transfer of Epimedium brevicornum and Epimedium pubescens by near infrared spectroscopy.关键词:Epimedium brevicornum;Epimedium pubescens;near infrared spectroscopy;quantitative analysis;model transfer348|91|0更新时间:2025-06-09
摘要:Epimedium brevicornum and Epimedium pubescens are commonly used traditional Chinese medicines,and their active ingredients such as epimedin A,epimedin B,epimedin C and icariin have important effects on pharmacological effects. In this study,the desktop and portable near-infrared spectral data of Epimedium brevicornum and Epimedium pubescens were collected,and the content data of Epimedin A,Epimedin B,Epimedin C and Icariin were determined by HPLC,and then the partial least squares regression(PLSR) model and support vector regression(SVR) model were established. In order to realize the model adaptation and transfer between desktop near-infrared spectral data and portable near-infrared spectral data,two standard sample set selection methods were explored in the study:hierarchical clustering method and SPXY algorithm,and two model transfer methods were applied:direct correction(DS) method and piecewise direct correction(PDS) method. The results show that the standard sample set selection method and the model transfer method have significant impacts on the model transfer effect. Further verification by paired t test showed that there was no significant difference between the predicted value and the real value of the optimal transfer model (P > 0.05),which indicated that the established transfer model had good adaptability among different instruments. This study provides a basis for the quantitative analysis and model transfer of Epimedium brevicornum and Epimedium pubescens by near infrared spectroscopy.关键词:Epimedium brevicornum;Epimedium pubescens;near infrared spectroscopy;quantitative analysis;model transfer348|91|0更新时间:2025-06-09 -
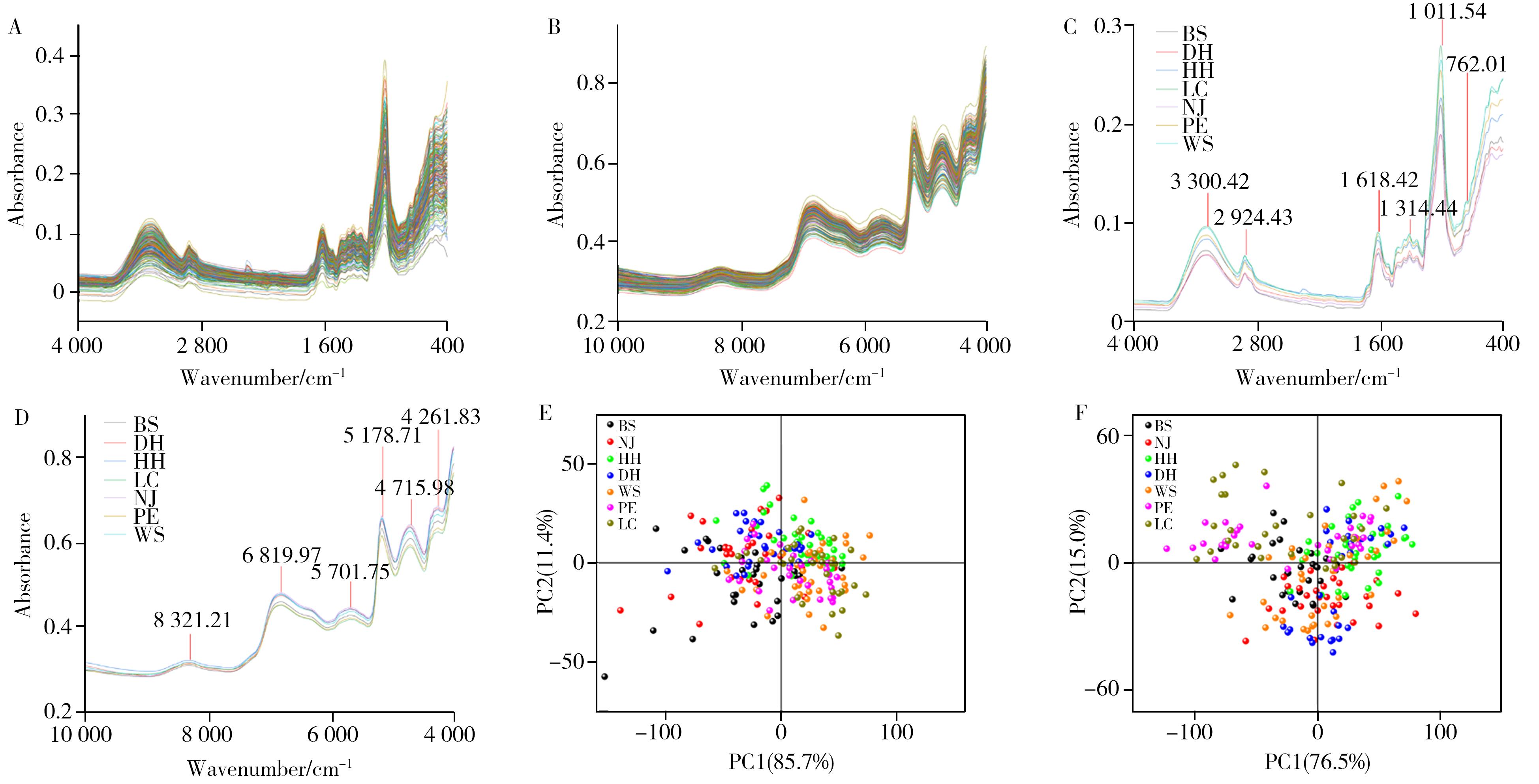
 摘要:Dendrobium officinale(D. officinale)is a precious plant with homology between medicine and food plant. Rapid and accurate identification of its geographical origin is essential to protect consumer rights and maintain market order. In order to realize rapid and effective identification of the geographical origin of D. officinale,a geographical traceability model of D. officinale was established based on attenuated total reflection Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy(ATR-FTIR) and Fourier transform near infrared spectroscopy(FT-NIR) technology,combined with data fusion strategy and chemometric methods. The results showed that the partial least squares discriminant analysis(PLS-DA) and support vector machine(SVM) models constructed on the FT-NIR and FT-NIR+ATR-FTIR fusion datasets after second derivative(2nd) preprocessing performed the best,with test set accuracy reaching 100.00%. The residual convolutional neural network(ResNet) model constructed based on two-dimensional correlation spectroscopy(2DCOS) achieved 100.00% accuracy on the training,testing and external validation sets. This study provides a scientific basis for geographical traceability of D. officinale and protection of geographical indication products.关键词:Dendrobium officinale;chemometrics;machine learning;2DCOS;geographical origin282|73|0更新时间:2025-06-09
摘要:Dendrobium officinale(D. officinale)is a precious plant with homology between medicine and food plant. Rapid and accurate identification of its geographical origin is essential to protect consumer rights and maintain market order. In order to realize rapid and effective identification of the geographical origin of D. officinale,a geographical traceability model of D. officinale was established based on attenuated total reflection Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy(ATR-FTIR) and Fourier transform near infrared spectroscopy(FT-NIR) technology,combined with data fusion strategy and chemometric methods. The results showed that the partial least squares discriminant analysis(PLS-DA) and support vector machine(SVM) models constructed on the FT-NIR and FT-NIR+ATR-FTIR fusion datasets after second derivative(2nd) preprocessing performed the best,with test set accuracy reaching 100.00%. The residual convolutional neural network(ResNet) model constructed based on two-dimensional correlation spectroscopy(2DCOS) achieved 100.00% accuracy on the training,testing and external validation sets. This study provides a scientific basis for geographical traceability of D. officinale and protection of geographical indication products.关键词:Dendrobium officinale;chemometrics;machine learning;2DCOS;geographical origin282|73|0更新时间:2025-06-09 -
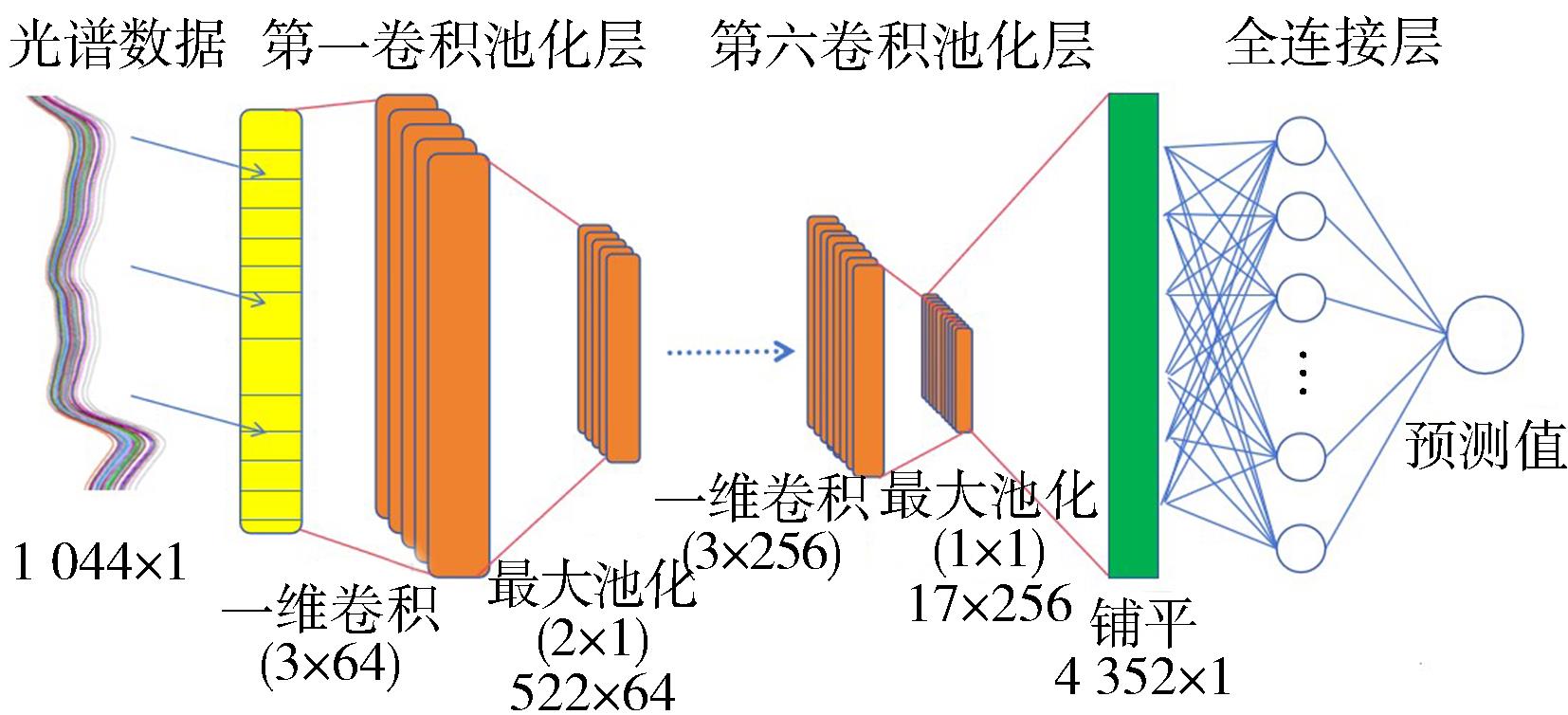 摘要:Hepatitis B surface antigen(HBsAg) is an important marker of hepatitis B virus infection. In this article,a novel method of reagent-free visible-near-infrared(Vis-NIR) spectral pattern recognition for serum HBsAg infection was studied. A total of 1 243 clinical serum samples(HBsAg positive 601 and negative 642) were collected,and a training-prediction-validation experimental design was used. A novel CNN integrated algorithm based on multi-cale convolution,SE Net attention mechanism and multi-scale dilated convolutions was constructed,which together with the classic partial least squares-discriminant analysis(PLS-DA) and the ordinary shallow CNN algorithm,were used to establish the Vis-NIR spectral discrimination model for HBsAg positive and negative serums. The standard normal variable(SNV) transform was used for spectral preprocessing. The PLS-DA and new types of CNN models based on the SNV spectra of near-infrared region(780-1 118nm) achieved significantly better modeling results,and the sensitivity(SEN) of the new CNN model reached a significantly higher 99.3%,and the false negative rate(FNR) reached a significantly lower 0.7%. The results show the feasibility of using serum Vis-NIR spectra to accurately identify HBsAg infection,and the proposed new types of deep learning algorithm is also promising for application in other spectral analysis fields.关键词:visible-near-infrared spectral pattern recognition;serum HBsAg infection diagnosis;partial least squares discriminant analysis(PLS-DA);convolutional neural network(CNN);SE Net attention mechanism;multiscale dilated convolution227|56|0更新时间:2025-06-09
摘要:Hepatitis B surface antigen(HBsAg) is an important marker of hepatitis B virus infection. In this article,a novel method of reagent-free visible-near-infrared(Vis-NIR) spectral pattern recognition for serum HBsAg infection was studied. A total of 1 243 clinical serum samples(HBsAg positive 601 and negative 642) were collected,and a training-prediction-validation experimental design was used. A novel CNN integrated algorithm based on multi-cale convolution,SE Net attention mechanism and multi-scale dilated convolutions was constructed,which together with the classic partial least squares-discriminant analysis(PLS-DA) and the ordinary shallow CNN algorithm,were used to establish the Vis-NIR spectral discrimination model for HBsAg positive and negative serums. The standard normal variable(SNV) transform was used for spectral preprocessing. The PLS-DA and new types of CNN models based on the SNV spectra of near-infrared region(780-1 118nm) achieved significantly better modeling results,and the sensitivity(SEN) of the new CNN model reached a significantly higher 99.3%,and the false negative rate(FNR) reached a significantly lower 0.7%. The results show the feasibility of using serum Vis-NIR spectra to accurately identify HBsAg infection,and the proposed new types of deep learning algorithm is also promising for application in other spectral analysis fields.关键词:visible-near-infrared spectral pattern recognition;serum HBsAg infection diagnosis;partial least squares discriminant analysis(PLS-DA);convolutional neural network(CNN);SE Net attention mechanism;multiscale dilated convolution227|56|0更新时间:2025-06-09 -
 摘要:To address the limitations of traditional microalgae detection methods,which rely on manual microscopy,result in prolonged analysis times,and produce results that are highly susceptible to the technical expertise of personnel,an integrated image preprocessing strategy combined with an enhanced YOLOv8 deep learning model for microalgae identification was proposed. A multi-method integration strategy of Gaussian fuzzy,Laplacian operator and principal component analysis was used to preprocess microalgae images. In the improved model,the SPD-Conv module was incorporated to mitigate the loss of fine-grained information,thereby improving the detection performance for low-resolution images and small-sized microalgae. A slim-neck architecture was employed to reduce the parameter count and model size,while the SimSPPF was introduced to expedite model convergence and enhance operational efficiency. The experimental results demonstrated that the multi-method integrated preprocessing strategy was able to substantially reduce image noise,and enhance the definition of microalgal contours. Under identical conditions,the improved YOLOv8 model achieved a mean average precision(mAP) of 92.2%,representing a 5.1% improvement over the original YOLOv8 model. Especially,it demonstrated superior performance in detecting small-sized microalgae. In comparison to Faster-RCNN,SSD,RTDETR-l,YOLOv3,YOLOv5,YOLOv6 and YOLOv7 models,the mAP of improved YOLOv8 model increased by 40.2%,6.8%,14.5%,1.2%,5.7%,4.7% and 0.8%,respectively. This method offers valuable insights for advancing microalgae species detection technology.关键词:Microalgae identification;Image preprocessing;YOLOv8 model;deep learning349|216|0更新时间:2025-06-09
摘要:To address the limitations of traditional microalgae detection methods,which rely on manual microscopy,result in prolonged analysis times,and produce results that are highly susceptible to the technical expertise of personnel,an integrated image preprocessing strategy combined with an enhanced YOLOv8 deep learning model for microalgae identification was proposed. A multi-method integration strategy of Gaussian fuzzy,Laplacian operator and principal component analysis was used to preprocess microalgae images. In the improved model,the SPD-Conv module was incorporated to mitigate the loss of fine-grained information,thereby improving the detection performance for low-resolution images and small-sized microalgae. A slim-neck architecture was employed to reduce the parameter count and model size,while the SimSPPF was introduced to expedite model convergence and enhance operational efficiency. The experimental results demonstrated that the multi-method integrated preprocessing strategy was able to substantially reduce image noise,and enhance the definition of microalgal contours. Under identical conditions,the improved YOLOv8 model achieved a mean average precision(mAP) of 92.2%,representing a 5.1% improvement over the original YOLOv8 model. Especially,it demonstrated superior performance in detecting small-sized microalgae. In comparison to Faster-RCNN,SSD,RTDETR-l,YOLOv3,YOLOv5,YOLOv6 and YOLOv7 models,the mAP of improved YOLOv8 model increased by 40.2%,6.8%,14.5%,1.2%,5.7%,4.7% and 0.8%,respectively. This method offers valuable insights for advancing microalgae species detection technology.关键词:Microalgae identification;Image preprocessing;YOLOv8 model;deep learning349|216|0更新时间:2025-06-09 -
 摘要:Based on near infrared spectroscopy combined with chemometrics methods,this study systematically studied the origin identification and model transfer of Epimedium brevicornum and Epimedium pubescens. Firstly,principal component analysis(PCA) was used to explore the spectral differences between the two,which provides a reference for subsequent classification modeling. Subsequently,support vector machine(SVM) and random forest(RF) classification models were established,and the effects of different spectral preprocessing methods were compared to screen out the best preprocessing combination(SG+1st Der+SNV and SG+2nd Der+SNV). Finally,a high-accuracy primitive identification model(the identification accuracy was 100%) was obtained. On this basis,the DS and PDS methods were used to correct the model,and the standard samples were selected by hierarchical clustering(HC),which successfully improved the adaptability and migration effect of the model. The results showed that the SVM model was superior to the RF model in terms of classification accuracy and migration stability,which provided a scientific basis for the application of portable near infrared spectrometer in the identification of traditional Chinese medicine.关键词:Epimedium brevicornum;Epimedium pubescens;near infrared spectroscopy;source identification;model transfer282|11|0更新时间:2025-06-09
摘要:Based on near infrared spectroscopy combined with chemometrics methods,this study systematically studied the origin identification and model transfer of Epimedium brevicornum and Epimedium pubescens. Firstly,principal component analysis(PCA) was used to explore the spectral differences between the two,which provides a reference for subsequent classification modeling. Subsequently,support vector machine(SVM) and random forest(RF) classification models were established,and the effects of different spectral preprocessing methods were compared to screen out the best preprocessing combination(SG+1st Der+SNV and SG+2nd Der+SNV). Finally,a high-accuracy primitive identification model(the identification accuracy was 100%) was obtained. On this basis,the DS and PDS methods were used to correct the model,and the standard samples were selected by hierarchical clustering(HC),which successfully improved the adaptability and migration effect of the model. The results showed that the SVM model was superior to the RF model in terms of classification accuracy and migration stability,which provided a scientific basis for the application of portable near infrared spectrometer in the identification of traditional Chinese medicine.关键词:Epimedium brevicornum;Epimedium pubescens;near infrared spectroscopy;source identification;model transfer282|11|0更新时间:2025-06-09 -
 摘要:In this study,Fourier transform near-infrared spectroscopy(FT-NIR),attenuated total reflection-Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy(ATR-FTIR) and two-dimensional correlation spectroscopy(2DCOS) techniques,combined with chemometric and deep learning were adopted to establish partial least squares discriminant analysis(PLS-DA) and Residual convolution neural network(ResNet)discriminant models for rapid and accurate traceability of A.tsaoko samples from seven main production areas(221 samples). The results indicated that the PLS-DA model established after the second derivative(2nd) + standard normal variate(SNV) preprocessing of ATR-FTIR spectral data showed the best performance(95.31%),but the optimal preprocessing for FT-NIR spectral data was 2nd. The ResNet model based on FT-NIR and ATR-FTIR synchronized 2DCOS images could achieve 100% accuracy without the need for optimal preprocessing and complex data conversion. Among them,the ResNet model established for 2DCOS images converted from FT-NIR had the least number of epochs,the shortest time consumption,and the lowest cost. This study provides a fast and accurate new method for identifying A.tsaoko from different geographical origins,laying the foundation for further research on the quality rating system of A.tsaoko.关键词:Amomum tsaoko;chemometrics;machine learning;2DCOS;geographical origin429|91|0更新时间:2025-06-09
摘要:In this study,Fourier transform near-infrared spectroscopy(FT-NIR),attenuated total reflection-Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy(ATR-FTIR) and two-dimensional correlation spectroscopy(2DCOS) techniques,combined with chemometric and deep learning were adopted to establish partial least squares discriminant analysis(PLS-DA) and Residual convolution neural network(ResNet)discriminant models for rapid and accurate traceability of A.tsaoko samples from seven main production areas(221 samples). The results indicated that the PLS-DA model established after the second derivative(2nd) + standard normal variate(SNV) preprocessing of ATR-FTIR spectral data showed the best performance(95.31%),but the optimal preprocessing for FT-NIR spectral data was 2nd. The ResNet model based on FT-NIR and ATR-FTIR synchronized 2DCOS images could achieve 100% accuracy without the need for optimal preprocessing and complex data conversion. Among them,the ResNet model established for 2DCOS images converted from FT-NIR had the least number of epochs,the shortest time consumption,and the lowest cost. This study provides a fast and accurate new method for identifying A.tsaoko from different geographical origins,laying the foundation for further research on the quality rating system of A.tsaoko.关键词:Amomum tsaoko;chemometrics;machine learning;2DCOS;geographical origin429|91|0更新时间:2025-06-09 -
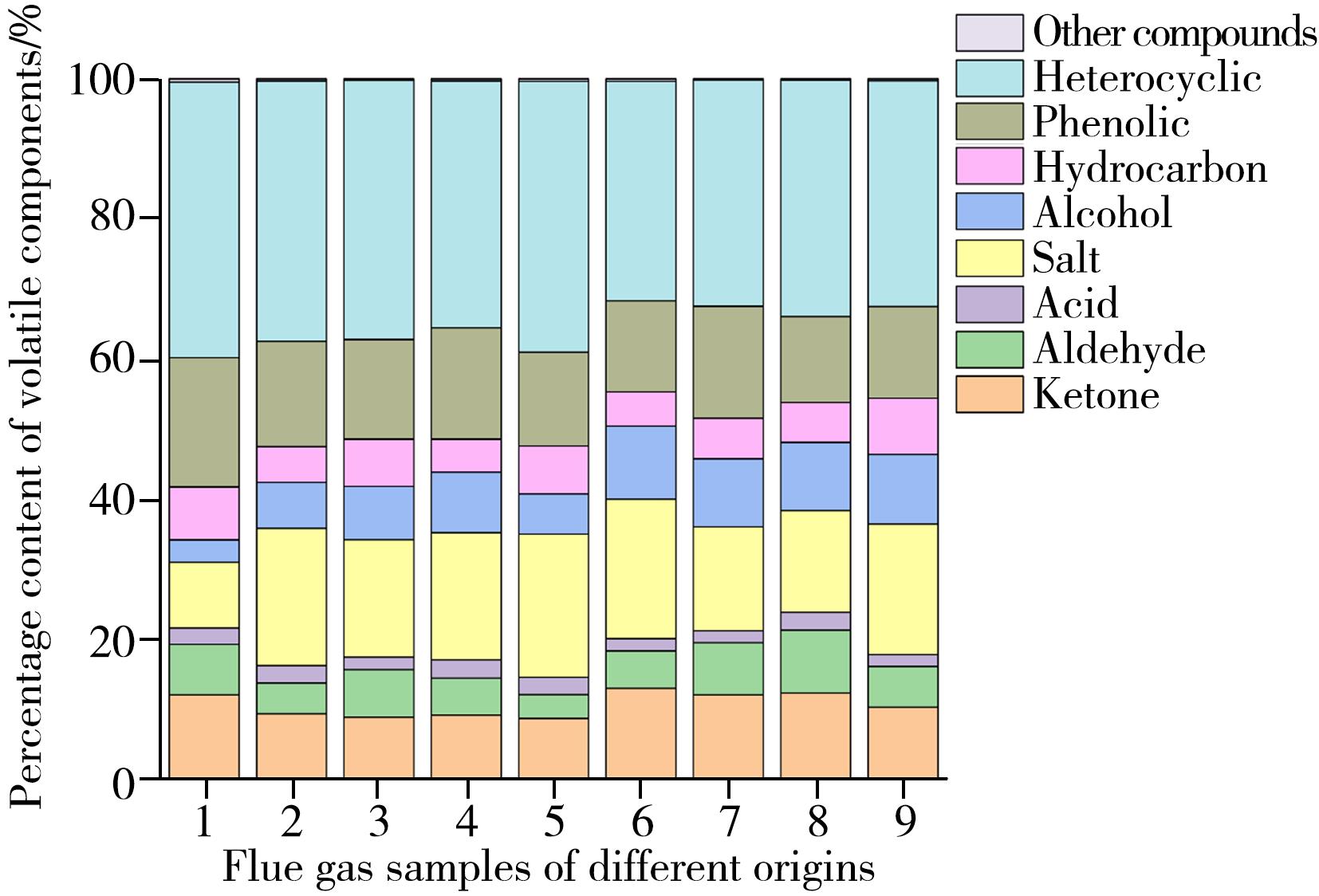 摘要:In order to understand the characteristic aroma components of honey-sweet-flavor tobacco smoke from different producing areas in Guizhou,the volatile compounds of 9 smoke samples were identified and analyzed using cambridge filter trapping combined with gas chromatography-olfactometer-mass spectrometry(GC-O-MS).Multivariate statistical methods combined with relative odor activity value(ROAV) were used to screen the characteristic aroma components of honey-sweet aroma in tobacco smoke,and the intrinsic material basis of the honey-sweet flavor of Guizhou tobacco was explored. The results showed that GC-MS identified a total of 144 volatile components,including 31 ketones,22 hydrocarbons,22 heterocyclics,22 phenols,15 esters,13 acids,11 alcohols,6 aldehydes and 2 other components. A total of 69 aroma compounds were identified by GC-O-MS,and the aroma characteristics mainly showed fruity,milky,caramelized,floral,nutty and honey-sweet aromas,and 25 aroma-active compounds(ROAV≥1) such as 1-penten-3-one,benzyl acetate,guaiacol,and ethyl-damascenone were screened out. Through orthogonal partial least squares discriminant analysis(OPLS-DA) analysis,a total of 34 key differential volatile aroma compounds with VIP>1 were screened. Combined with the conditions of VIP>1(P<0.05) and ROAV≥1,8 characteristic aroma components were obtained,including 1-penten-3-one,methylcyclopentenolone,ethylcyclopentenolone,p-isopropylphenol,eugenol,indole,trans-nerolidol and ethyl-damascenone. The partial least squares regression(PLSR) results further verified that these 8 aroma substances had an important contribution to the formation of the overall aroma profile and were the key aroma compounds of the sweet aroma of Guizhou tobacco leaves. This study used GC-O-MS technology,ROAV value and multivariate statistical methods to screen out the key aroma substances in the sweet aroma of tobacco smoke,providing a reference for clarifying the aroma characteristics of tobacco smoke in Guizhou.关键词:Guizhou tobacco;honey-sweet aroma;gas chromatography-olfactometer-mass spectrometry;relative odor activity value;multivariate statistical analysis;characteristic odorant318|75|0更新时间:2025-06-09
摘要:In order to understand the characteristic aroma components of honey-sweet-flavor tobacco smoke from different producing areas in Guizhou,the volatile compounds of 9 smoke samples were identified and analyzed using cambridge filter trapping combined with gas chromatography-olfactometer-mass spectrometry(GC-O-MS).Multivariate statistical methods combined with relative odor activity value(ROAV) were used to screen the characteristic aroma components of honey-sweet aroma in tobacco smoke,and the intrinsic material basis of the honey-sweet flavor of Guizhou tobacco was explored. The results showed that GC-MS identified a total of 144 volatile components,including 31 ketones,22 hydrocarbons,22 heterocyclics,22 phenols,15 esters,13 acids,11 alcohols,6 aldehydes and 2 other components. A total of 69 aroma compounds were identified by GC-O-MS,and the aroma characteristics mainly showed fruity,milky,caramelized,floral,nutty and honey-sweet aromas,and 25 aroma-active compounds(ROAV≥1) such as 1-penten-3-one,benzyl acetate,guaiacol,and ethyl-damascenone were screened out. Through orthogonal partial least squares discriminant analysis(OPLS-DA) analysis,a total of 34 key differential volatile aroma compounds with VIP>1 were screened. Combined with the conditions of VIP>1(P<0.05) and ROAV≥1,8 characteristic aroma components were obtained,including 1-penten-3-one,methylcyclopentenolone,ethylcyclopentenolone,p-isopropylphenol,eugenol,indole,trans-nerolidol and ethyl-damascenone. The partial least squares regression(PLSR) results further verified that these 8 aroma substances had an important contribution to the formation of the overall aroma profile and were the key aroma compounds of the sweet aroma of Guizhou tobacco leaves. This study used GC-O-MS technology,ROAV value and multivariate statistical methods to screen out the key aroma substances in the sweet aroma of tobacco smoke,providing a reference for clarifying the aroma characteristics of tobacco smoke in Guizhou.关键词:Guizhou tobacco;honey-sweet aroma;gas chromatography-olfactometer-mass spectrometry;relative odor activity value;multivariate statistical analysis;characteristic odorant318|75|0更新时间:2025-06-09 -
 摘要:In this study,we explored the combination of machine learning techniques and square wave anodic stripping voltammetry(SWASV) to improve the simultaneous detection of four heavy metal ions:Cd2+,Pb2+,Cu2+,and Hg2+. Traditional electrochemical methods mainly rely on finding a linear response interval within a certain concentration range when detecting heavy metal ions,and in a multi-ionic environment,the SWASV curve often interferes,resulting in reduced accuracy. In this study,bare glassy carbon electrodes were used to detect repeatable SWASV of different concentrations of metal ion solutions,and important parameters such as current value,peak voltage and peak area were extracted from the detection data,and the concentration prediction model was constructed by combining extreme gradient boosting(XGBoost) and random forest(RF),and the support vector machine(SVM) was used. Among the machine learning classification algorithms,the SVR algorithm has the best effect (the area under the ROC curve of the four ions is greater than 0.95),and the fit degree(R-Squared) between the predicted value and the true value of the XGBoost concentration prediction model of the RF model is more than 0.95. By combining SWASV and machine learning,it is possible to achieve high-precision ion detection in complex ion mixing systems and improve the reliability of detection results. The results of this study provide an innovative solution for environmental monitoring and contamination control of multiple heavy metal ions,and demonstrate the application potential of machine learning in the field of electrochemical analysis.关键词:electrochemistry;heavy metal ions;machine learning;interference analysis169|42|0更新时间:2025-06-09
摘要:In this study,we explored the combination of machine learning techniques and square wave anodic stripping voltammetry(SWASV) to improve the simultaneous detection of four heavy metal ions:Cd2+,Pb2+,Cu2+,and Hg2+. Traditional electrochemical methods mainly rely on finding a linear response interval within a certain concentration range when detecting heavy metal ions,and in a multi-ionic environment,the SWASV curve often interferes,resulting in reduced accuracy. In this study,bare glassy carbon electrodes were used to detect repeatable SWASV of different concentrations of metal ion solutions,and important parameters such as current value,peak voltage and peak area were extracted from the detection data,and the concentration prediction model was constructed by combining extreme gradient boosting(XGBoost) and random forest(RF),and the support vector machine(SVM) was used. Among the machine learning classification algorithms,the SVR algorithm has the best effect (the area under the ROC curve of the four ions is greater than 0.95),and the fit degree(R-Squared) between the predicted value and the true value of the XGBoost concentration prediction model of the RF model is more than 0.95. By combining SWASV and machine learning,it is possible to achieve high-precision ion detection in complex ion mixing systems and improve the reliability of detection results. The results of this study provide an innovative solution for environmental monitoring and contamination control of multiple heavy metal ions,and demonstrate the application potential of machine learning in the field of electrochemical analysis.关键词:electrochemistry;heavy metal ions;machine learning;interference analysis169|42|0更新时间:2025-06-09 -
 摘要:The rapid identification of natural unknown minerals in the field is limited by three challenges:differences in the resolution of different spectral devices,weak model generalization ability due to insufficient sample size,and limited ability to extract high-dimensional complex spectral features. To address these three challenges,this paper designs and implements a Raman spectroscopy classification model that combines a multi-scale convolutional neural network with spectral sample generation. This model is integrated with a portable Raman spectrometer to enable rapid identification of unknown minerals in the field. First,a cubic spline curve fitting algorithm was used to match the dimensions of the spectra collected by different devices,thereby eliminating differences in sampling resolution between different spectral devices. Second,5 668 spectral samples of 1 648 mineral types in the global mineral spectral database were fed into a generative adversarial network for training,producing 15 000 augmented samples to alleviate the constraints of data scarcity on model classification performance. Finally,a new multi-scale deep convolutional network was used to synchronously extract the broad and narrow peak features of Raman spectra,thereby enhancing the characterization capability of complex spectra. In addition,the model proposed in this paper was compared with several classic machine learning models,such as k-nearest neighbor(k-NN),support vector machine(SVM),and random forest(RF),to evaluate their performance in identifying unknown minerals. The experimental results demonstrate that the proposed multi-scale convolutional neural network combined with spectral sample generation achieves significantly higher accuracy in classifying Raman spectra of unknown minerals compared to other traditional machine learning models,with top-1 and top-3 accuracy rates of 93.26% and 98.94%,respectively. The proposed model was applied to identify 50 types of unknown natural mineral samples using a portable Raman spectroscopy system,achieving an accuracy rate of 100%. The identification time for a single sample was only 1-2 min,demonstrating the advantages of the method proposed in this paper,which includes rapid,accurate,and sample-free analysis.关键词:Raman spectroscopy;Mineral Identification;Resampling method;Multi-scale convolutional networks;Sample generation based on CGAN249|35|0更新时间:2025-06-09
摘要:The rapid identification of natural unknown minerals in the field is limited by three challenges:differences in the resolution of different spectral devices,weak model generalization ability due to insufficient sample size,and limited ability to extract high-dimensional complex spectral features. To address these three challenges,this paper designs and implements a Raman spectroscopy classification model that combines a multi-scale convolutional neural network with spectral sample generation. This model is integrated with a portable Raman spectrometer to enable rapid identification of unknown minerals in the field. First,a cubic spline curve fitting algorithm was used to match the dimensions of the spectra collected by different devices,thereby eliminating differences in sampling resolution between different spectral devices. Second,5 668 spectral samples of 1 648 mineral types in the global mineral spectral database were fed into a generative adversarial network for training,producing 15 000 augmented samples to alleviate the constraints of data scarcity on model classification performance. Finally,a new multi-scale deep convolutional network was used to synchronously extract the broad and narrow peak features of Raman spectra,thereby enhancing the characterization capability of complex spectra. In addition,the model proposed in this paper was compared with several classic machine learning models,such as k-nearest neighbor(k-NN),support vector machine(SVM),and random forest(RF),to evaluate their performance in identifying unknown minerals. The experimental results demonstrate that the proposed multi-scale convolutional neural network combined with spectral sample generation achieves significantly higher accuracy in classifying Raman spectra of unknown minerals compared to other traditional machine learning models,with top-1 and top-3 accuracy rates of 93.26% and 98.94%,respectively. The proposed model was applied to identify 50 types of unknown natural mineral samples using a portable Raman spectroscopy system,achieving an accuracy rate of 100%. The identification time for a single sample was only 1-2 min,demonstrating the advantages of the method proposed in this paper,which includes rapid,accurate,and sample-free analysis.关键词:Raman spectroscopy;Mineral Identification;Resampling method;Multi-scale convolutional networks;Sample generation based on CGAN249|35|0更新时间:2025-06-09 -
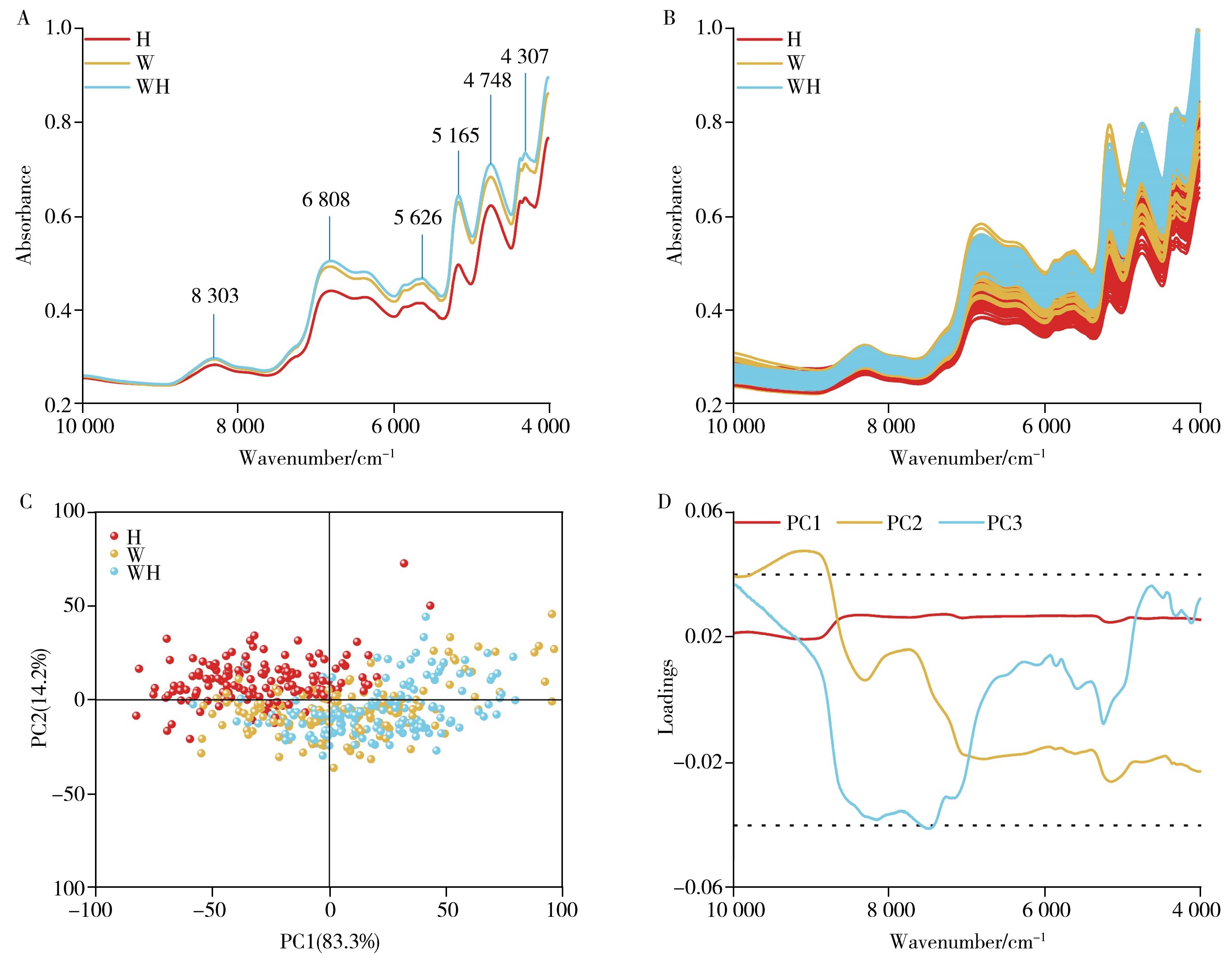 摘要:In this study,a partial least squares discriminant analysis(PLS-DA) model and a residual convolution neural network(ResNet) model were constructed using Fourier transform near-infrared spectroscopy(FT-NIR) and two-dimensional correlation spectroscopy(2DCOS) technology,in conjunction with chemometric methods and deep learning algorithms,to rapidly and accurately identify three cultivated varieties of Gastrodia elata Blum(G.elata Bl.) samples(447). The results showed that the PLS-DA model,created by integrating first derivativ (1st Der) and multiple scatter correction(MSC) preprocessing of FT-NIR data,demonstrated the highest stability and the best overall performance,with an accuracy of 99.00%. At the same time,the identification method based on FT-NIR synchronous 2DCOS image combined with ResNet model could achieve rapid and accurate identification(100.00% accuracy) of different cultivars of G. elata Bl without the need for optimal pretreatment and complex data conversion. This study provides a rapid and accurate method for identifying different cultivars of G. elata Bl.,and lays a foundation for further germplasm resource research and breeding of new variety.关键词:Fourier transform near-infrared spectroscopy;chemometrics;machine learning;Gastrodia elata Blum;cultivar42|74|0更新时间:2025-06-09
摘要:In this study,a partial least squares discriminant analysis(PLS-DA) model and a residual convolution neural network(ResNet) model were constructed using Fourier transform near-infrared spectroscopy(FT-NIR) and two-dimensional correlation spectroscopy(2DCOS) technology,in conjunction with chemometric methods and deep learning algorithms,to rapidly and accurately identify three cultivated varieties of Gastrodia elata Blum(G.elata Bl.) samples(447). The results showed that the PLS-DA model,created by integrating first derivativ (1st Der) and multiple scatter correction(MSC) preprocessing of FT-NIR data,demonstrated the highest stability and the best overall performance,with an accuracy of 99.00%. At the same time,the identification method based on FT-NIR synchronous 2DCOS image combined with ResNet model could achieve rapid and accurate identification(100.00% accuracy) of different cultivars of G. elata Bl without the need for optimal pretreatment and complex data conversion. This study provides a rapid and accurate method for identifying different cultivars of G. elata Bl.,and lays a foundation for further germplasm resource research and breeding of new variety.关键词:Fourier transform near-infrared spectroscopy;chemometrics;machine learning;Gastrodia elata Blum;cultivar42|74|0更新时间:2025-06-09 -
 摘要:A qualitative model for rapid screening of metronidazole,ketoconazole,chloramphenicol and norfloxacin in acne-clearing cosmetics was developed based on ultraviolet spectrum of cosmetics combined with machine learning algorithms. In this study,ultraviolet spectra of 167 batches of acne-clearing cosmetics were collected for model building. The two-dimensional correlation spectroscopy(2D-COS) technique was used for ultraviolet spectra feature band selection,and the effect of each model was compared under 22 spectral preprocessing methods,three machine learning algorithms,and three dataset division ratios. Five-classification qualitative models were established for positive and negative samples containing metronidazole,ketoconazole,chloramphenicol and norfloxacin,respectively.The results showed that the ultraviolet spectra of 190-360 nm were selected to be processed jointly by standard normal variables(SNV) and Savitzky-Golay convolutional smoothing(SG),and the ratio of training set to prediction set division of 7∶3 was chosen to build a qualitative classification model using the error back propagation(BP) neural network algorithm. The accuracy of the model training set and prediction set can reach 96.58% and 98.00%,respectively,with good prediction and generalisation ability. This method can effectively screen and identify the four banned anti-infective drugs in cosmetics quickly and accurately,which not only saves the detection cost and time and improves the detection efficiency,but also helps the on-site rapid inspection and provides a rapid and intelligent solution for the detection of illegal addition of banned substances in cosmetics.关键词:ultraviolet spectroscopy;cosmetics;error back propagation neural network;random forest;support vector machines;two-dimensional correlation spectroscopy309|65|0更新时间:2025-06-09
摘要:A qualitative model for rapid screening of metronidazole,ketoconazole,chloramphenicol and norfloxacin in acne-clearing cosmetics was developed based on ultraviolet spectrum of cosmetics combined with machine learning algorithms. In this study,ultraviolet spectra of 167 batches of acne-clearing cosmetics were collected for model building. The two-dimensional correlation spectroscopy(2D-COS) technique was used for ultraviolet spectra feature band selection,and the effect of each model was compared under 22 spectral preprocessing methods,three machine learning algorithms,and three dataset division ratios. Five-classification qualitative models were established for positive and negative samples containing metronidazole,ketoconazole,chloramphenicol and norfloxacin,respectively.The results showed that the ultraviolet spectra of 190-360 nm were selected to be processed jointly by standard normal variables(SNV) and Savitzky-Golay convolutional smoothing(SG),and the ratio of training set to prediction set division of 7∶3 was chosen to build a qualitative classification model using the error back propagation(BP) neural network algorithm. The accuracy of the model training set and prediction set can reach 96.58% and 98.00%,respectively,with good prediction and generalisation ability. This method can effectively screen and identify the four banned anti-infective drugs in cosmetics quickly and accurately,which not only saves the detection cost and time and improves the detection efficiency,but also helps the on-site rapid inspection and provides a rapid and intelligent solution for the detection of illegal addition of banned substances in cosmetics.关键词:ultraviolet spectroscopy;cosmetics;error back propagation neural network;random forest;support vector machines;two-dimensional correlation spectroscopy309|65|0更新时间:2025-06-09
Scientific Papers
-
 摘要:Qingke liquor,a renowned Tibetan alcoholic beverage derived from hull-less highland barley exclusively cultivated in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau,has witnessed a surge in sales. However,the issue of adulteration has emerged as a pressing concern demanding immediate attention. The research focused on the rapid identification methods of 'Huzhu' brand Qingke liquor,a geographical indication protection product,using ultra-violet(UV) spectroscopy. Two approaches were proposed:principal component analysis-support vector machine(PCA-SVM) and multi-model partial least squares-discriminant analysis(MPLS-DA). Three categories of liquors are considered:Chinese 'Huzhu' Qingke liquor(CHQL),other brand Qingke liquor(OBQL),and non-Qingke-based liquor(NQBL). SVM was performed using two principal components to solve the binary classification problem,while PLS1 algorithm is used for each column of the dummy variable Y in MPLS-DA to integrate prediction results from submodels. Both PCA-SVM and MPLS-DA successfully built discrimination models for CHQL. PCA-SVM distinguishes CHQL from OBQL and NQBL but cannot differentiate between OBQL and NQBL. In contrast,MPLS-DA correctly identified all three classes of samples,and it could solve multi-classification problems. These results demonstrate that the proposed method can serve as a simple and rapid identification approach for CHQL,with MPLS-DA exhibiting superior sample recognition capabilities.关键词:Chinese Huzhu Qingke Liquor;ultra-violet spectroscopy;chemometrics;discriminant analysis316|49|0更新时间:2025-06-09
摘要:Qingke liquor,a renowned Tibetan alcoholic beverage derived from hull-less highland barley exclusively cultivated in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau,has witnessed a surge in sales. However,the issue of adulteration has emerged as a pressing concern demanding immediate attention. The research focused on the rapid identification methods of 'Huzhu' brand Qingke liquor,a geographical indication protection product,using ultra-violet(UV) spectroscopy. Two approaches were proposed:principal component analysis-support vector machine(PCA-SVM) and multi-model partial least squares-discriminant analysis(MPLS-DA). Three categories of liquors are considered:Chinese 'Huzhu' Qingke liquor(CHQL),other brand Qingke liquor(OBQL),and non-Qingke-based liquor(NQBL). SVM was performed using two principal components to solve the binary classification problem,while PLS1 algorithm is used for each column of the dummy variable Y in MPLS-DA to integrate prediction results from submodels. Both PCA-SVM and MPLS-DA successfully built discrimination models for CHQL. PCA-SVM distinguishes CHQL from OBQL and NQBL but cannot differentiate between OBQL and NQBL. In contrast,MPLS-DA correctly identified all three classes of samples,and it could solve multi-classification problems. These results demonstrate that the proposed method can serve as a simple and rapid identification approach for CHQL,with MPLS-DA exhibiting superior sample recognition capabilities.关键词:Chinese Huzhu Qingke Liquor;ultra-violet spectroscopy;chemometrics;discriminant analysis316|49|0更新时间:2025-06-09 -
 摘要:The issue of heavy metal contamination in soil sediment is becoming increasingly prevalent. The development of on-site rapid detection methods for heavy metal elements represents the only viable approach to achieving effective pollution monitoring and environmental governance. Accordingly,this study proposed a quantitative analysis method for heavy metal elements in soil sediments based on laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy combined with machine learning algorithms. Firstly,the spectral collection of soil sediment samples was completed using the constructed LIBS device,and the efficacy of various spectral preprocessing techniques on spectral data preprocessing was investigated. Subsequently,feature variable selection was conducted on the preprocessed spectral data,based on the measurement of variable importance. The preprocessing method,variable importance threshold,and other parameters were optimized using cross-validation. A quantitative analysis model for three heavy metal elements(Pb,Cu and Zn) in soil sediment samples was constructed based on optimized input variables. To further validate the performance of the model,a comparison was conducted with the performance of other calibration models. The results indicate that the VIM-RF calibration model proposed in this study exhibits the best predictive performance,with a R2p of 0.993 0 and a RMSEp of 0.029 8 mg/kg for Pb,a R2p of 0.981 0 and a RMSEp of 0.112 7 mg/kg for Cu,and a R2p of 0.992 0 and a RMSEp of 0.166 2 mg/kg for Zn. It can be seen that the method established by this research institute is expected to provide a theoretical reference for the rapid screening and treatment of heavy metal pollution in soil sediment environments.关键词:soil sediment;heavy metals;laser induced breakdown spectroscopy;random forest;feature selection278|29|0更新时间:2025-06-09
摘要:The issue of heavy metal contamination in soil sediment is becoming increasingly prevalent. The development of on-site rapid detection methods for heavy metal elements represents the only viable approach to achieving effective pollution monitoring and environmental governance. Accordingly,this study proposed a quantitative analysis method for heavy metal elements in soil sediments based on laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy combined with machine learning algorithms. Firstly,the spectral collection of soil sediment samples was completed using the constructed LIBS device,and the efficacy of various spectral preprocessing techniques on spectral data preprocessing was investigated. Subsequently,feature variable selection was conducted on the preprocessed spectral data,based on the measurement of variable importance. The preprocessing method,variable importance threshold,and other parameters were optimized using cross-validation. A quantitative analysis model for three heavy metal elements(Pb,Cu and Zn) in soil sediment samples was constructed based on optimized input variables. To further validate the performance of the model,a comparison was conducted with the performance of other calibration models. The results indicate that the VIM-RF calibration model proposed in this study exhibits the best predictive performance,with a R2p of 0.993 0 and a RMSEp of 0.029 8 mg/kg for Pb,a R2p of 0.981 0 and a RMSEp of 0.112 7 mg/kg for Cu,and a R2p of 0.992 0 and a RMSEp of 0.166 2 mg/kg for Zn. It can be seen that the method established by this research institute is expected to provide a theoretical reference for the rapid screening and treatment of heavy metal pollution in soil sediment environments.关键词:soil sediment;heavy metals;laser induced breakdown spectroscopy;random forest;feature selection278|29|0更新时间:2025-06-09 -
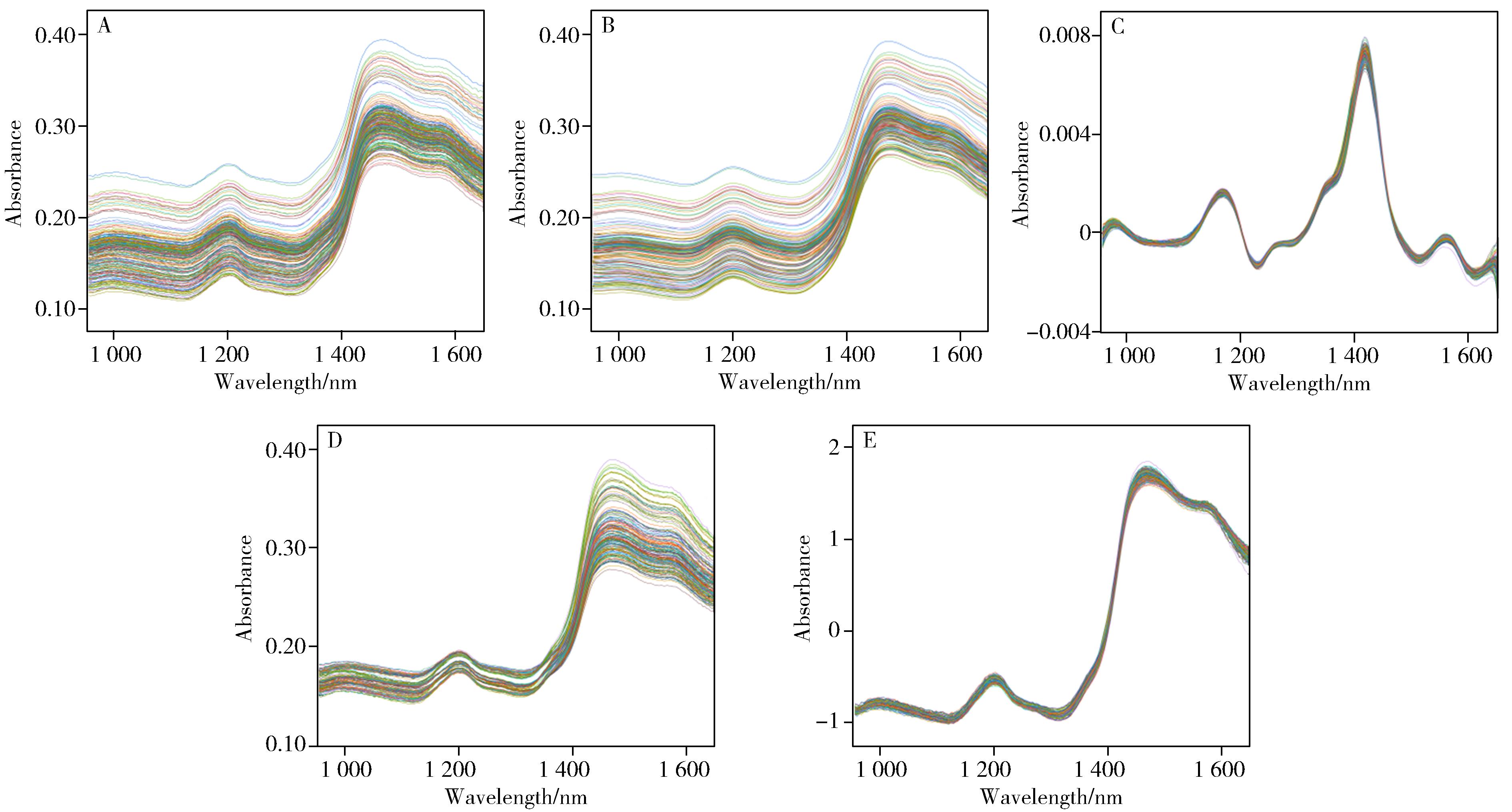 摘要:Rapid and low-cost detection tools provide new methods for the qualitative and quantitative analysis of microplastics(MPs)in chicken feed. In this study,a portable near infrared(NIR)spectrometer was used for qualitative and quantitative analysis of MPs-contaminated chicken feed samples. A total of 244 chicken feed samples were prepared,including 61 non-contaminated chicken feed samples and 183 MPs-contaminated chicken feed samples(mass fraction range of 0.01%-0.8%)namely polypropylene(PP),polyvinyl chloride(PVC) and polyethylene terephthalate(PET),respectively. The NIR spectra of all samples were collected based on the portable NIR spectrometer(wavelength range,900-1 700 nm). 1/3 of the samples were randomly selected as the prediction set,and the remaining 2/3 of the samples were used as the calibration set. The mathematical model for qualitative and quantitative analysis of MPs in chicken feed was developed using the partial least squares method. For the qualitative models:the model built by the multiple scattering treatment showed the best performance. The discrimination accuracies were 99.38% and 100% for the samples in the calibration and prediction sets,respectively. For quantitative partial least squares regression(PLSR)models:genetic algorithms(GA)showed significant advantages in wavelength selection for improving the prediction performance of the PLSR models for MPs in chicken feed. The GA-PLSR model predicted correlation coefficients(Rp) more than 0.873 7 and residual prediction deviation ratios(RPD) more than 2.709 0 for the three MPs. The results showed that it was feasible to analyze MPs in chicken feed by qualitative and quantitative analysis based on portable NIR spectroscopy. This study provides a low-cost and rapid method for the detection of MPs in feed.关键词:portable near infrared spectrometer;microplastics(MPs);chicken feed;chemometrics;qualitative and quantitative analysis404|80|0更新时间:2025-06-09
摘要:Rapid and low-cost detection tools provide new methods for the qualitative and quantitative analysis of microplastics(MPs)in chicken feed. In this study,a portable near infrared(NIR)spectrometer was used for qualitative and quantitative analysis of MPs-contaminated chicken feed samples. A total of 244 chicken feed samples were prepared,including 61 non-contaminated chicken feed samples and 183 MPs-contaminated chicken feed samples(mass fraction range of 0.01%-0.8%)namely polypropylene(PP),polyvinyl chloride(PVC) and polyethylene terephthalate(PET),respectively. The NIR spectra of all samples were collected based on the portable NIR spectrometer(wavelength range,900-1 700 nm). 1/3 of the samples were randomly selected as the prediction set,and the remaining 2/3 of the samples were used as the calibration set. The mathematical model for qualitative and quantitative analysis of MPs in chicken feed was developed using the partial least squares method. For the qualitative models:the model built by the multiple scattering treatment showed the best performance. The discrimination accuracies were 99.38% and 100% for the samples in the calibration and prediction sets,respectively. For quantitative partial least squares regression(PLSR)models:genetic algorithms(GA)showed significant advantages in wavelength selection for improving the prediction performance of the PLSR models for MPs in chicken feed. The GA-PLSR model predicted correlation coefficients(Rp) more than 0.873 7 and residual prediction deviation ratios(RPD) more than 2.709 0 for the three MPs. The results showed that it was feasible to analyze MPs in chicken feed by qualitative and quantitative analysis based on portable NIR spectroscopy. This study provides a low-cost and rapid method for the detection of MPs in feed.关键词:portable near infrared spectrometer;microplastics(MPs);chicken feed;chemometrics;qualitative and quantitative analysis404|80|0更新时间:2025-06-09 -
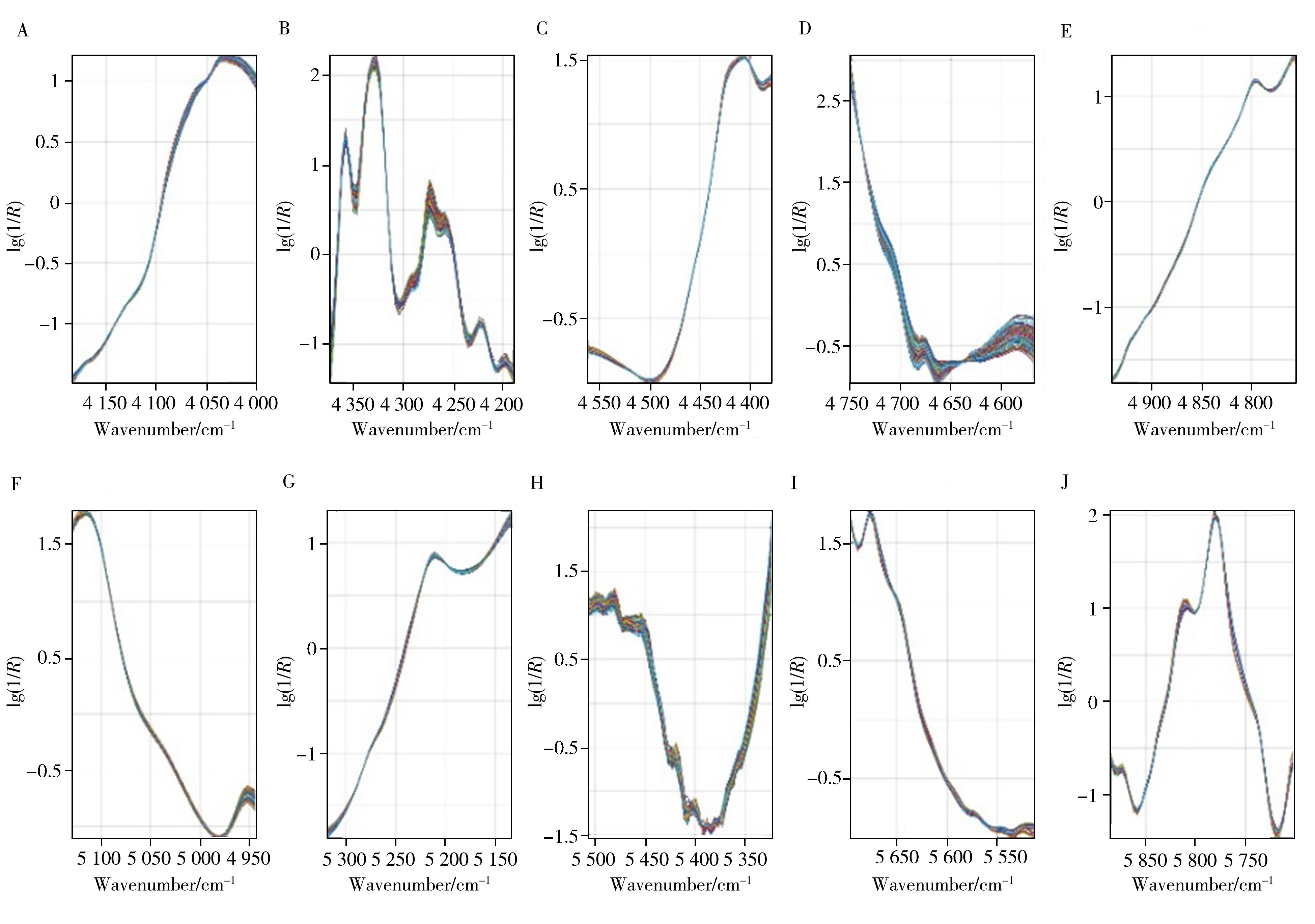 摘要:The qualitative identification of fake drugs based on near-infrared(NIR) spectroscopy needs to extract characteristic information and establish prediction models from complex,overlapped and unstable spectra by using computers and chemometrics. In this kind of task,there may also be an imbalanced classification problem where there are relatively few samples of a certain class. Based on the generation of virtual samples and ensemble modeling,this approach has the potential to improve the recognition accuracy for imbalanced training set. In this paper,azithromycin was taken as the research object,a group of experimental samples were designed,and an ensemble algorithm of partial least squares discriminant analysis(PLS-DA) based on virtual samples was proposed to construct a classifier for identifying whether a drug sample had expired. The performance of single and ensemble models was compared in ten different spectral ranges,and the influence of different imbalance ratios,the composition of minority class samples and ensemble size were also discussed. The sensitivity of ensemble models was improved by about 9% on average. Finally,the overall effectiveness of the ensemble learning strategy was confirmed. The proposed ensemble algorithm shows more advantages when there are too few minority class samples,and the method can also be used for other types of systems.关键词:virtual samples;ensemble;near-infrared spectroscopy;drug;identification321|34|0更新时间:2025-06-09
摘要:The qualitative identification of fake drugs based on near-infrared(NIR) spectroscopy needs to extract characteristic information and establish prediction models from complex,overlapped and unstable spectra by using computers and chemometrics. In this kind of task,there may also be an imbalanced classification problem where there are relatively few samples of a certain class. Based on the generation of virtual samples and ensemble modeling,this approach has the potential to improve the recognition accuracy for imbalanced training set. In this paper,azithromycin was taken as the research object,a group of experimental samples were designed,and an ensemble algorithm of partial least squares discriminant analysis(PLS-DA) based on virtual samples was proposed to construct a classifier for identifying whether a drug sample had expired. The performance of single and ensemble models was compared in ten different spectral ranges,and the influence of different imbalance ratios,the composition of minority class samples and ensemble size were also discussed. The sensitivity of ensemble models was improved by about 9% on average. Finally,the overall effectiveness of the ensemble learning strategy was confirmed. The proposed ensemble algorithm shows more advantages when there are too few minority class samples,and the method can also be used for other types of systems.关键词:virtual samples;ensemble;near-infrared spectroscopy;drug;identification321|34|0更新时间:2025-06-09 -
Blood Species Identification Method and Model Evaluation Based on Volatile Organic Compounds Testing
 摘要:Blood species identification(BSI) plays a significant role in criminal investigation,import and export inspection,animal protection and other fields. Volatilomics analysis of blood volatile organic compounds (VOCs) is a novel approach for blood species identification. To screen potential biomarkers of blood from different species,the study established multiple machine learning(ML) classification algorithms,and compared the predictive value of different classification models for blood species identification. Headspace solid-phase microextraction(HS-SPME) coupled with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry(GC-MS) was used to analyze VOCs in the blood of eight common species. Partial least squares discriminant analysis(PLS-DA) and orthogonal partial least squares discriminant analysis(OPLS-DA) were employed to screen potential biomarkers. Samples were randomly divided into training and testing sets at a ratio of 7∶3. Nine common classification models were established,and the best algorithm was selected and optimized by comparing all models. A model using all VOCs as variables was constructed to verify the reliability of the potential biomarkers,and different resampling methods were used to assess the impact of training and testing set division on the model. A total of 17 VOCs related to species characteristics of human and seven different animal bloods were screened. The accuracy of the multi-layer perceptron,naive Bayes algorithm,multinomial logistic regression algorithm,K-nearest neighbor(KNN) algorithm,Gaussian kernel function support vector machine,polynomial kernel function support vector machine,decision tree,random forest model,and extreme gradient boosting tree model were 0.859 7,0.575 1,0.859 7,0.942 1,0.815 0,0.734 2,0.842 9,0.923 1 and 0.872 9,respectively. Among them,the accuracy,area under the receiver operating characteristic curve(AUC),and Brier score of the KNN model under the testing set were 0.918 4,0.999 0 and 0.037 6. KNN was selected as the optimal algorithm,and the best model's hyperparameter combination was:K value of 5,distance-weighted kernel function of the triweight function,and the Minkowski distance parameter p of 0.324 0. The best-performing model on the validation set achieved an accuracy of 0.928 4,with corresponding metrics of 0.997 0 for the AUC and 0.057 6 for the Brier score. There was no significant difference in the results between the model using all component variables and the potential biomarker variable model(t-test p>0.05),and there was no significant difference in the results of models using different resampling methods(t-test p>0.05). Volatilomics analysis shows great potential in blood species identification,with strong reliability of potential biomarkers,high model accuracy,and strong anti-interference ability.关键词:headspace solid-phase microextraction(HS-SPME)/gas chromatography-mass spectrometry(GC-MS);volatile organic compounds(VOCs);blood species identification(BSI);volatomics;machine learning(ML)206|55|0更新时间:2025-06-09
摘要:Blood species identification(BSI) plays a significant role in criminal investigation,import and export inspection,animal protection and other fields. Volatilomics analysis of blood volatile organic compounds (VOCs) is a novel approach for blood species identification. To screen potential biomarkers of blood from different species,the study established multiple machine learning(ML) classification algorithms,and compared the predictive value of different classification models for blood species identification. Headspace solid-phase microextraction(HS-SPME) coupled with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry(GC-MS) was used to analyze VOCs in the blood of eight common species. Partial least squares discriminant analysis(PLS-DA) and orthogonal partial least squares discriminant analysis(OPLS-DA) were employed to screen potential biomarkers. Samples were randomly divided into training and testing sets at a ratio of 7∶3. Nine common classification models were established,and the best algorithm was selected and optimized by comparing all models. A model using all VOCs as variables was constructed to verify the reliability of the potential biomarkers,and different resampling methods were used to assess the impact of training and testing set division on the model. A total of 17 VOCs related to species characteristics of human and seven different animal bloods were screened. The accuracy of the multi-layer perceptron,naive Bayes algorithm,multinomial logistic regression algorithm,K-nearest neighbor(KNN) algorithm,Gaussian kernel function support vector machine,polynomial kernel function support vector machine,decision tree,random forest model,and extreme gradient boosting tree model were 0.859 7,0.575 1,0.859 7,0.942 1,0.815 0,0.734 2,0.842 9,0.923 1 and 0.872 9,respectively. Among them,the accuracy,area under the receiver operating characteristic curve(AUC),and Brier score of the KNN model under the testing set were 0.918 4,0.999 0 and 0.037 6. KNN was selected as the optimal algorithm,and the best model's hyperparameter combination was:K value of 5,distance-weighted kernel function of the triweight function,and the Minkowski distance parameter p of 0.324 0. The best-performing model on the validation set achieved an accuracy of 0.928 4,with corresponding metrics of 0.997 0 for the AUC and 0.057 6 for the Brier score. There was no significant difference in the results between the model using all component variables and the potential biomarker variable model(t-test p>0.05),and there was no significant difference in the results of models using different resampling methods(t-test p>0.05). Volatilomics analysis shows great potential in blood species identification,with strong reliability of potential biomarkers,high model accuracy,and strong anti-interference ability.关键词:headspace solid-phase microextraction(HS-SPME)/gas chromatography-mass spectrometry(GC-MS);volatile organic compounds(VOCs);blood species identification(BSI);volatomics;machine learning(ML)206|55|0更新时间:2025-06-09 -
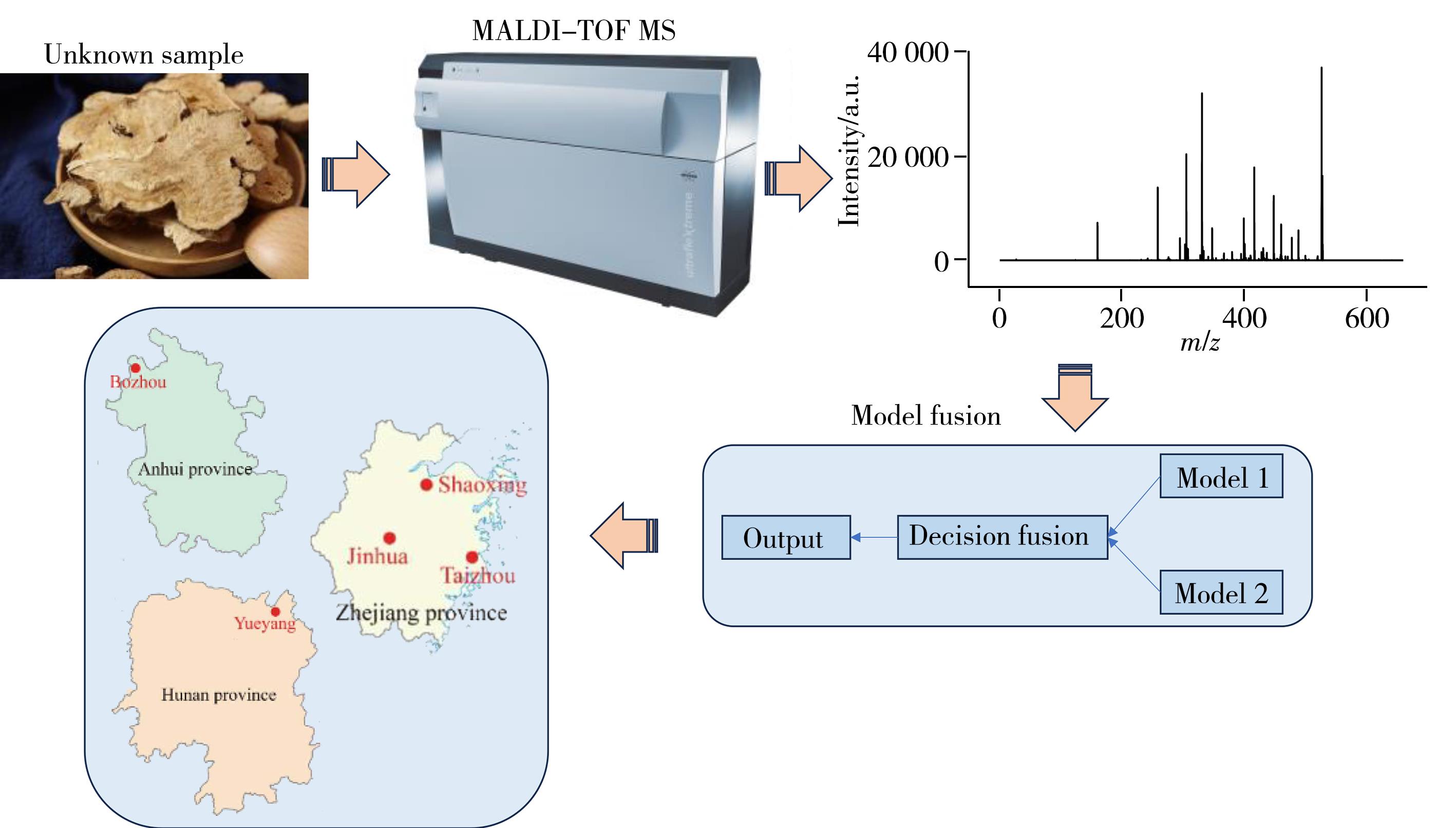 摘要:In this study,the matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time of flight mass spectrometry(MALDI-TOF MS) was used to analyze the geographical origin traceability of Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz. in combination with two improved random forest fusion algorithms. Firstly,mass spectrum data of Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz. samples from 3 provinces were obtained by MALDI-TOF MS,and the data size of each sample was 1×234 154. In view of the large amount of each sample data,the data were preliminarily simplified by data bins strategy(1×6 600). Then,the principal component analysis was carried out to reduce the dimension by set the threshold of cumulative variance contribution rate. The dimensionality reduction data were used to construct the adaptive enhanced extreme random forest model(AERF) and the adaptive enhanced balanced random forest model(ABRF). Finally,AERF-ABRF model was obtained through model fusion strategy to trace the origin of Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz.. The results showed that the adaptive enhanced random forest model combined with model fusion strategy based on dimensionality reduction of data proposed in this study could accurately distinguish the samples from 3 provinces,and achieved correct classification rate(CCR) values of 100% for both the validation and test sample sets. At the same time,compared to individual models,the model fusion strategy exhibited a much higher correct classification rate.关键词:random forest;model fusion;Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz.;geographical origin traceability;matrix-assisted laser desorption-ionization time of flight mass spectrometry(MALDI-TOF MS)318|9|0更新时间:2025-06-09
摘要:In this study,the matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time of flight mass spectrometry(MALDI-TOF MS) was used to analyze the geographical origin traceability of Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz. in combination with two improved random forest fusion algorithms. Firstly,mass spectrum data of Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz. samples from 3 provinces were obtained by MALDI-TOF MS,and the data size of each sample was 1×234 154. In view of the large amount of each sample data,the data were preliminarily simplified by data bins strategy(1×6 600). Then,the principal component analysis was carried out to reduce the dimension by set the threshold of cumulative variance contribution rate. The dimensionality reduction data were used to construct the adaptive enhanced extreme random forest model(AERF) and the adaptive enhanced balanced random forest model(ABRF). Finally,AERF-ABRF model was obtained through model fusion strategy to trace the origin of Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz.. The results showed that the adaptive enhanced random forest model combined with model fusion strategy based on dimensionality reduction of data proposed in this study could accurately distinguish the samples from 3 provinces,and achieved correct classification rate(CCR) values of 100% for both the validation and test sample sets. At the same time,compared to individual models,the model fusion strategy exhibited a much higher correct classification rate.关键词:random forest;model fusion;Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz.;geographical origin traceability;matrix-assisted laser desorption-ionization time of flight mass spectrometry(MALDI-TOF MS)318|9|0更新时间:2025-06-09 -
 摘要:Varietal differences significantly affect the soluble solid content(SSC) and near-infrared spectroscopy(NIRS) characteristics of apples,creating challenges when applying SSC spectral calibration models developed for one variety to others. This study developed a partial least squares regression(PLSR) calibration model using Aksu Fuji apples(Batch 1) and addressed the practical challenge of predicting SSC in Qingdao Scarlet apples(Batch 2) through model updating methods. The PLSR model,created with a combination of first derivative(1D) preprocessing and competitive adaptive reweighted sampling(CARS),effectively predicted SSC for Batch 1,achieving a correlation coefficient of prediction(Rp) of 0.972 8 and a root mean square error of prediction(RMSEP) of 0.383 8 °Brix. However,the Batch 1 model performed poorly in predicting SSC for Batch 2. To address this limitation,three model updating methods—calibration updating,slope/bias correction(SBC),and dynamic orthogonal projection(DOP)—were applied,and the impact of different update sample sizes was evaluated. Results showed that RMSEP significantly decreased after model updating. Among the methods,SBC performed best,reducing the RMSEP for Batch 2 from 1.075 6 °Brix to 0.233 4 °Brix with 20 new samples. These findings demonstrate that model updating effectively improves prediction performance across different apple varieties,enhancing model robustness and offering valuable guidance for maintaining and updating SSC detection models in practical applications.关键词:apple;soluble solids content;near-infrared spectroscopy;PLSR model;model update241|57|0更新时间:2025-06-09
摘要:Varietal differences significantly affect the soluble solid content(SSC) and near-infrared spectroscopy(NIRS) characteristics of apples,creating challenges when applying SSC spectral calibration models developed for one variety to others. This study developed a partial least squares regression(PLSR) calibration model using Aksu Fuji apples(Batch 1) and addressed the practical challenge of predicting SSC in Qingdao Scarlet apples(Batch 2) through model updating methods. The PLSR model,created with a combination of first derivative(1D) preprocessing and competitive adaptive reweighted sampling(CARS),effectively predicted SSC for Batch 1,achieving a correlation coefficient of prediction(Rp) of 0.972 8 and a root mean square error of prediction(RMSEP) of 0.383 8 °Brix. However,the Batch 1 model performed poorly in predicting SSC for Batch 2. To address this limitation,three model updating methods—calibration updating,slope/bias correction(SBC),and dynamic orthogonal projection(DOP)—were applied,and the impact of different update sample sizes was evaluated. Results showed that RMSEP significantly decreased after model updating. Among the methods,SBC performed best,reducing the RMSEP for Batch 2 from 1.075 6 °Brix to 0.233 4 °Brix with 20 new samples. These findings demonstrate that model updating effectively improves prediction performance across different apple varieties,enhancing model robustness and offering valuable guidance for maintaining and updating SSC detection models in practical applications.关键词:apple;soluble solids content;near-infrared spectroscopy;PLSR model;model update241|57|0更新时间:2025-06-09 -
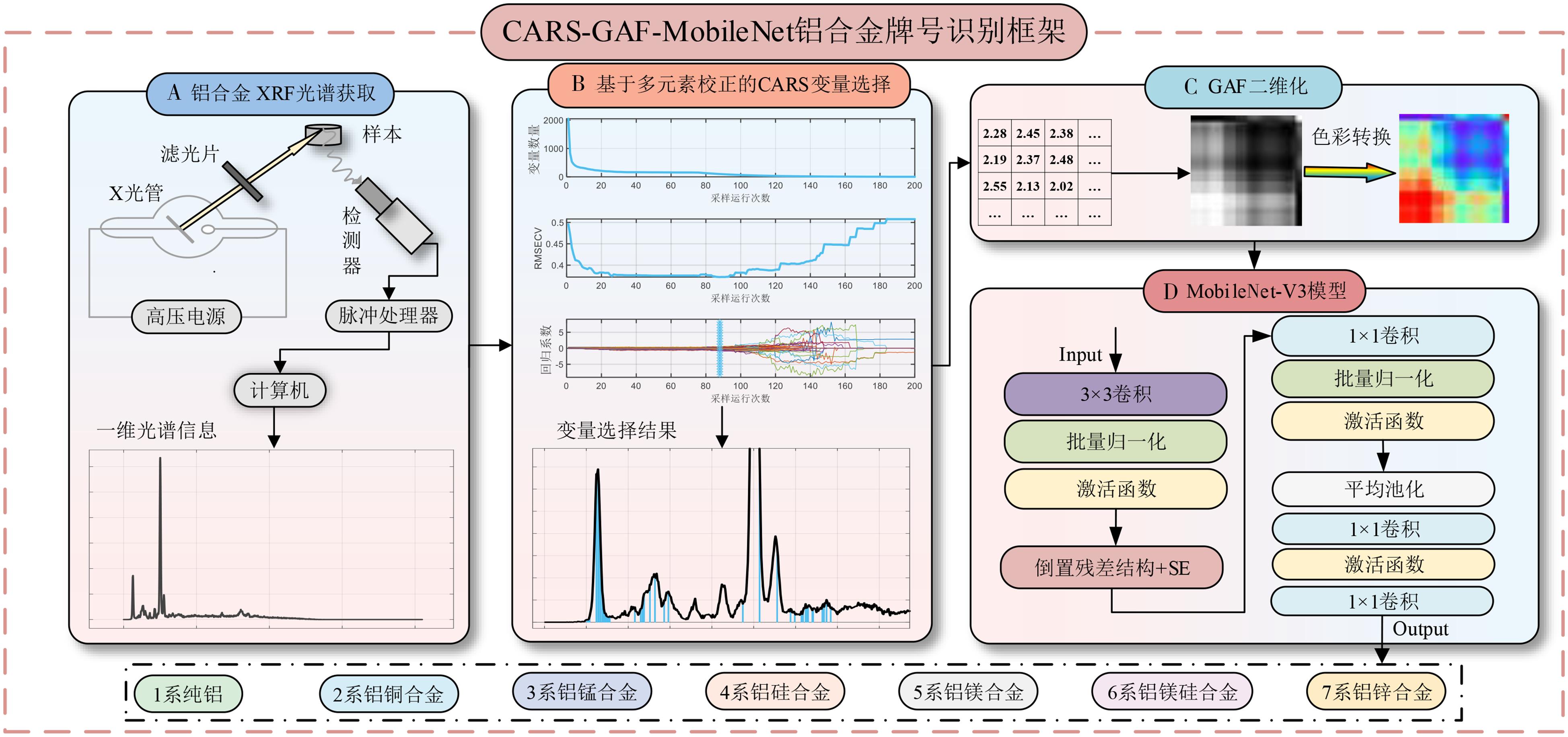 摘要:Aluminum alloys are widely used in industry due to their excellent characteristics,and accurate classification of aluminum alloys grades can further promote the development of manufacturing and other fields. In this paper,a new aluminum alloy X-ray fluorescence(XRF) spectral classification framework CARS-GAF-MobileNet(CGM)was proposed. First,an XRF spectrometer was used to obtain XRF spectral data of the aluminum alloy samples. Then,a multi-element calibration-based competitive adaptive reweighted sampling(CARS) was proposed to select variables for the data. Next,the one-dimensional spectra were converted into two-dimensional spectral images using Gramian angular field(GAF),and the grayscale images were converted into RGB images by color mapping. Finally,the converted 2D spectral images were inputs to the Mobilenet-V3 model to classify the aluminum alloy samples. The experimental results showed that the final classification accuracy of the proposed CGM framework could reach 94.3%,which could accurately identify aluminum alloy samples of different grades. The CGM is a promising framework for identifying aluminum alloy grades,and it has superior theoretical guidance and application value for the aluminum alloy classification problem.关键词:X-ray fluorescence;aluminum alloy classification;Gramian angular field;competitive adaptive reweighted sampling;deep learning211|59|0更新时间:2025-06-09
摘要:Aluminum alloys are widely used in industry due to their excellent characteristics,and accurate classification of aluminum alloys grades can further promote the development of manufacturing and other fields. In this paper,a new aluminum alloy X-ray fluorescence(XRF) spectral classification framework CARS-GAF-MobileNet(CGM)was proposed. First,an XRF spectrometer was used to obtain XRF spectral data of the aluminum alloy samples. Then,a multi-element calibration-based competitive adaptive reweighted sampling(CARS) was proposed to select variables for the data. Next,the one-dimensional spectra were converted into two-dimensional spectral images using Gramian angular field(GAF),and the grayscale images were converted into RGB images by color mapping. Finally,the converted 2D spectral images were inputs to the Mobilenet-V3 model to classify the aluminum alloy samples. The experimental results showed that the final classification accuracy of the proposed CGM framework could reach 94.3%,which could accurately identify aluminum alloy samples of different grades. The CGM is a promising framework for identifying aluminum alloy grades,and it has superior theoretical guidance and application value for the aluminum alloy classification problem.关键词:X-ray fluorescence;aluminum alloy classification;Gramian angular field;competitive adaptive reweighted sampling;deep learning211|59|0更新时间:2025-06-09 -
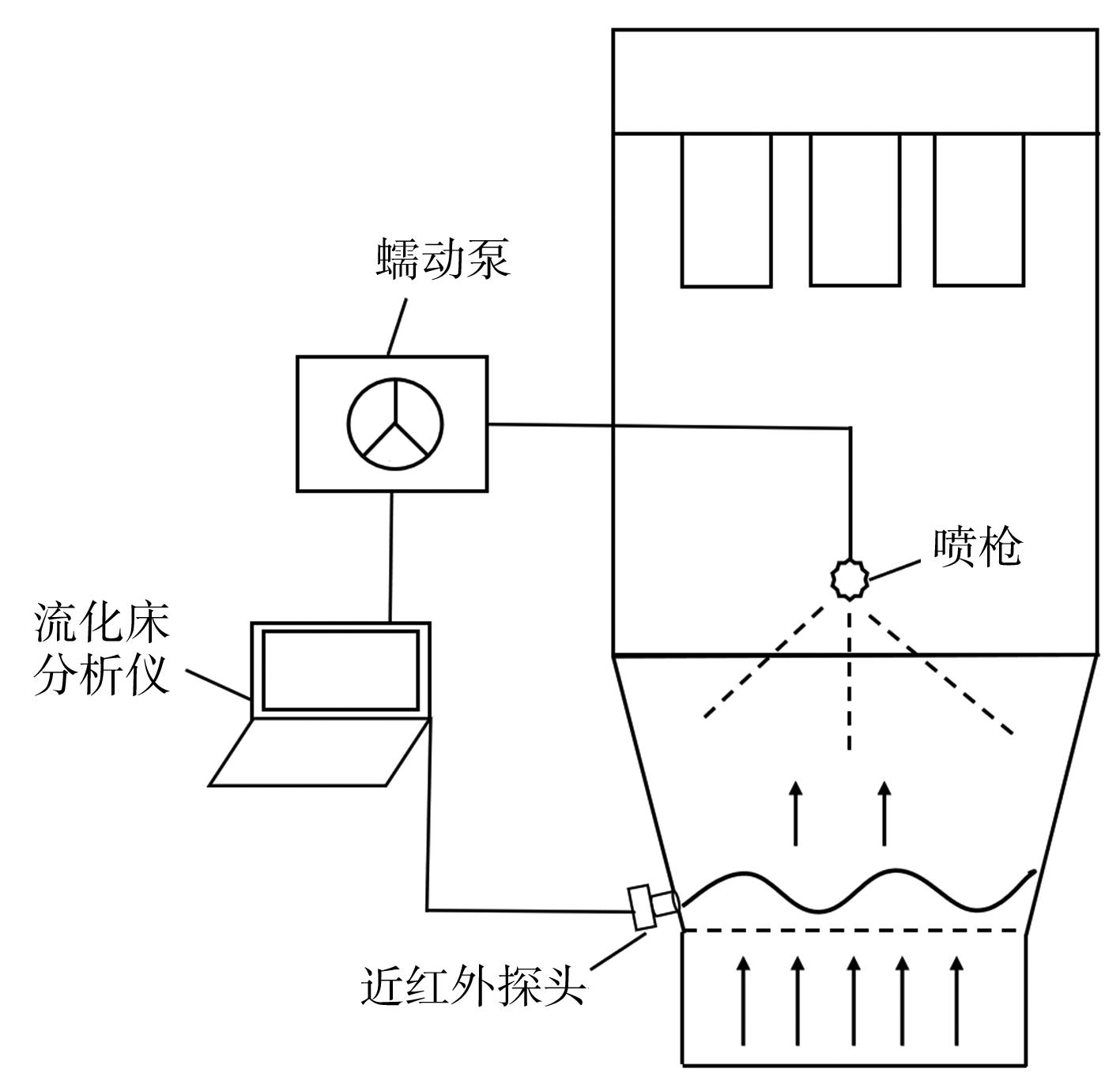 摘要:Fluidized bed granulation is widely used in the production of traditional Chinese medicine granules,but the traditional granulation process relies on the operator to observe the material state in the fluidized bed,and manually adjust the air volume and liquid injection speed according to experience,which has the problems of time-consuming,labor-intensive and insufficient intelligent level. Therefore,this paper constructed a fluidization state value feedback control system based on near infrared spectroscopy,and evaluated its control performance. The near infrared spectrum of the fluidized bed granulation process was collected in real time to analyze the movement state of the material and calculate the fluidization state value index. Then,the system automatically adjusted the peristaltic pump speed in the spray system according to the fluidization state value index and the preset control rules,thereby realizing the dynamic control of the spray speed and achieving the fluidization state value real-time feedback control. The experimental results show that the feedback control system can effectively prevent the occurrence of bed collapse when the fluidization state deteriorates. When the fluidization state value is good,the system can speed up the liquid spraying,thereby saving the granulation time and improving the production efficiency. Compared with the manual control mode,the automatic control system reduced the liquid injection time by more than 20%. In terms of fluidization state value control,the system is equivalent to the manual control,while it shows significant advantages in the optimization of liquid injection time. In addition,the control system shows good applicability and stability under the interference conditions of changing process conditions such as inlet air temperature,inlet air volume,atomization pressure,etc. Therefore,the fluidization state value feedback control system of fluidized bed granulation process based on near infrared spectroscopy established in this paper has stability and reliability,and can provide strong technical support for the intelligent manufacturing of fluidized bed granulation.关键词:near infrared spectroscopy;fluidized bed granulation;fluidization state value analysis;feedback control;automatic control311|75|0更新时间:2025-06-09
摘要:Fluidized bed granulation is widely used in the production of traditional Chinese medicine granules,but the traditional granulation process relies on the operator to observe the material state in the fluidized bed,and manually adjust the air volume and liquid injection speed according to experience,which has the problems of time-consuming,labor-intensive and insufficient intelligent level. Therefore,this paper constructed a fluidization state value feedback control system based on near infrared spectroscopy,and evaluated its control performance. The near infrared spectrum of the fluidized bed granulation process was collected in real time to analyze the movement state of the material and calculate the fluidization state value index. Then,the system automatically adjusted the peristaltic pump speed in the spray system according to the fluidization state value index and the preset control rules,thereby realizing the dynamic control of the spray speed and achieving the fluidization state value real-time feedback control. The experimental results show that the feedback control system can effectively prevent the occurrence of bed collapse when the fluidization state deteriorates. When the fluidization state value is good,the system can speed up the liquid spraying,thereby saving the granulation time and improving the production efficiency. Compared with the manual control mode,the automatic control system reduced the liquid injection time by more than 20%. In terms of fluidization state value control,the system is equivalent to the manual control,while it shows significant advantages in the optimization of liquid injection time. In addition,the control system shows good applicability and stability under the interference conditions of changing process conditions such as inlet air temperature,inlet air volume,atomization pressure,etc. Therefore,the fluidization state value feedback control system of fluidized bed granulation process based on near infrared spectroscopy established in this paper has stability and reliability,and can provide strong technical support for the intelligent manufacturing of fluidized bed granulation.关键词:near infrared spectroscopy;fluidized bed granulation;fluidization state value analysis;feedback control;automatic control311|75|0更新时间:2025-06-09 -
 摘要:The content of dry matter(DM) is one of the important indices to determine the quality of mango. In this paper,near-infrared spectroscopy(NIR) is used to predict the dry matter content of mango,so as to achieve rapid evaluation of mango quality. The study launched to propose the grid numericalization scheme for screening structural parameters based on the convolutional neural network(CNN) framework. The parameter optimization strategy was improved by the fusion of long short-term memory(LSTM) network,to propose the CNN-LSTM combined optimization model. In data experiment,a shallow CNN modeling architecture was constructed. The hyperparameters were for refine tuning by testing some local-scale values of the core parameters of CNN-LSTM model. Results showed that the optimal CNN model and CNN-LSTM models were obviously better than the conventional linear or nonlinear models in both the model training and model testing stages. In addition to identifying the most optimal models,we also provided some other appreciating less-optional models as well as their available parameter combinations. These findings are expected to be helpful in the production line of mango cultivation. The modeling framework of a shallow CNN architecture in fusion with the LSTM optimization provides chemometrics technical support for rapid detection of dry matter content in mango fruit.关键词:near-infrared(NIR) spectroscopy;dry matter of mango fruit;convolutional neural network(CNN);long short-term memory(LSTM);parameter optimization;grid numericalization317|77|0更新时间:2025-06-09
摘要:The content of dry matter(DM) is one of the important indices to determine the quality of mango. In this paper,near-infrared spectroscopy(NIR) is used to predict the dry matter content of mango,so as to achieve rapid evaluation of mango quality. The study launched to propose the grid numericalization scheme for screening structural parameters based on the convolutional neural network(CNN) framework. The parameter optimization strategy was improved by the fusion of long short-term memory(LSTM) network,to propose the CNN-LSTM combined optimization model. In data experiment,a shallow CNN modeling architecture was constructed. The hyperparameters were for refine tuning by testing some local-scale values of the core parameters of CNN-LSTM model. Results showed that the optimal CNN model and CNN-LSTM models were obviously better than the conventional linear or nonlinear models in both the model training and model testing stages. In addition to identifying the most optimal models,we also provided some other appreciating less-optional models as well as their available parameter combinations. These findings are expected to be helpful in the production line of mango cultivation. The modeling framework of a shallow CNN architecture in fusion with the LSTM optimization provides chemometrics technical support for rapid detection of dry matter content in mango fruit.关键词:near-infrared(NIR) spectroscopy;dry matter of mango fruit;convolutional neural network(CNN);long short-term memory(LSTM);parameter optimization;grid numericalization317|77|0更新时间:2025-06-09 -
Unconstrained MW-PLS Method for Vis-NIR Spectroscopy and Its Application in Serum Bilirubin Analysis
 摘要:Moving window-partial least squares(MW-PLS),using a constrained two-parameter search(initial wavelength,number of wavelengths) to traverse all sub-wavebands,is an effective waveband screening method of spectral analysis. In this study,MW-PLS was extended to unconstrained parametric search,denoted as unconstrained MW-PLS(UMW-PLS),which contained forward and backward optimizations,and could select dual-waveband combinations. The visible-near infrared (Vis-NIR) spectral analysis models of serum bilirubin indicators—indirect bilirubin (IBil),direct bilirubin(DBil) and total bilirubin(TBil) were established by MW-PLS and UMW-PLS methods,respectively. For each indicator,the selected optimal 2nd UMW-PLS and 3rd UMW-PLS models,corresponding separately the dual-waveband and three-waveband combinations,were strictly better than the optimal MW-PLS models,and the wavelength complexity decreased sequentially. In external validation,the ratio of performance-to-deviation(RPD) of the optimal 3rd UMW-PLS models of the three indicators reached 3.0,3.2 and 5.8,respectively. The results indicated that Vis-NIR spectroscopy can be used for the reagent-free simultaneous quantitative analysis of bilirubin indicators IBil,DBil and TBil. The proposed UMW-PLS was a concise and effective multi-waveband optimization strategy.关键词:visible-near infrared spectral analysis;indirect bilirubin;direct bilirubin;total bilirubin;unconstrained moving window-partial least squares;multi-waveband optimization strategy350|46|0更新时间:2025-06-09
摘要:Moving window-partial least squares(MW-PLS),using a constrained two-parameter search(initial wavelength,number of wavelengths) to traverse all sub-wavebands,is an effective waveband screening method of spectral analysis. In this study,MW-PLS was extended to unconstrained parametric search,denoted as unconstrained MW-PLS(UMW-PLS),which contained forward and backward optimizations,and could select dual-waveband combinations. The visible-near infrared (Vis-NIR) spectral analysis models of serum bilirubin indicators—indirect bilirubin (IBil),direct bilirubin(DBil) and total bilirubin(TBil) were established by MW-PLS and UMW-PLS methods,respectively. For each indicator,the selected optimal 2nd UMW-PLS and 3rd UMW-PLS models,corresponding separately the dual-waveband and three-waveband combinations,were strictly better than the optimal MW-PLS models,and the wavelength complexity decreased sequentially. In external validation,the ratio of performance-to-deviation(RPD) of the optimal 3rd UMW-PLS models of the three indicators reached 3.0,3.2 and 5.8,respectively. The results indicated that Vis-NIR spectroscopy can be used for the reagent-free simultaneous quantitative analysis of bilirubin indicators IBil,DBil and TBil. The proposed UMW-PLS was a concise and effective multi-waveband optimization strategy.关键词:visible-near infrared spectral analysis;indirect bilirubin;direct bilirubin;total bilirubin;unconstrained moving window-partial least squares;multi-waveband optimization strategy350|46|0更新时间:2025-06-09 -
 摘要:The contents of mineral elements in 255 batches of Citri Reticulatae Pericarpium from Xinhui and Guangxi were determined by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Orthogonal partial least squares discriminant analysis(OPLS-DA) was used to study the different elements in Citri Reticulatae Pericarpium from different producing areas. Four preprocessing methods,such as Z-score normalization,Min-Max normalization,mean normaliztion,and Max abs scaler,are used to establish a discriminant model by combining random forest(RF),decision tree(DT),support vector machine(SVM),and gradient boosting(GB) method. The results showed that among the 41 mineral elements,Na,Sn,Y,Ba,Er,Ho,Yb,Dy,Ni,Li,Gd,Tb,Sm,Nd,Rb were the main difference elements between Citri Reticulatae Pericarpium from Xinhui and Guangxi. Among the four machine learning models,the SVM model has the best prediction results. By SVM model,the accuracy of the training group and test group under the three processing methods of Z-score normalization,Min-Max normalization,and mean normalization was the same,which was 100% and 96%,respectively,and the F1 value of 0.96. These result reflected the high accuracy of this method. Based on mineral element content combined with machine learning,this study established a high accuracy and reliability method for the origin identification of Citri Reticulatae Pericarpium,which provided technical support for quality control of Citri Reticulatae Pericarpium and provided the basis for the origin traceability discrimination of traditional Chinese medicinal herbs.关键词:mineral elements;machine learning;Citri Reticulatae Pericarpium;origin identification293|69|0更新时间:2025-06-09
摘要:The contents of mineral elements in 255 batches of Citri Reticulatae Pericarpium from Xinhui and Guangxi were determined by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Orthogonal partial least squares discriminant analysis(OPLS-DA) was used to study the different elements in Citri Reticulatae Pericarpium from different producing areas. Four preprocessing methods,such as Z-score normalization,Min-Max normalization,mean normaliztion,and Max abs scaler,are used to establish a discriminant model by combining random forest(RF),decision tree(DT),support vector machine(SVM),and gradient boosting(GB) method. The results showed that among the 41 mineral elements,Na,Sn,Y,Ba,Er,Ho,Yb,Dy,Ni,Li,Gd,Tb,Sm,Nd,Rb were the main difference elements between Citri Reticulatae Pericarpium from Xinhui and Guangxi. Among the four machine learning models,the SVM model has the best prediction results. By SVM model,the accuracy of the training group and test group under the three processing methods of Z-score normalization,Min-Max normalization,and mean normalization was the same,which was 100% and 96%,respectively,and the F1 value of 0.96. These result reflected the high accuracy of this method. Based on mineral element content combined with machine learning,this study established a high accuracy and reliability method for the origin identification of Citri Reticulatae Pericarpium,which provided technical support for quality control of Citri Reticulatae Pericarpium and provided the basis for the origin traceability discrimination of traditional Chinese medicinal herbs.关键词:mineral elements;machine learning;Citri Reticulatae Pericarpium;origin identification293|69|0更新时间:2025-06-09 -
 摘要:This study selected 160 commercially available and laboratory-prepared E-liquid samples for spectral scanning using a Fourier transform near-infrared(NIR) spectrometer(Thermo Fisher,USA). By comparing with chemical reference values,the near-infrared spectroscopy(NIRS) technique was validated for accurate prediction of six components in E-liquids:benzoic acid,nicotine,WS-23,WS-3,propylene glycol,and glycerol. Utilizing TQ Analyst software,partial least squares(PLS) regression was employed to establish quantitative models for these additives. Spectral preprocessing involved first-derivative transformation combined with Savitzky-Golay smoothing,and optimal wavelength ranges were determined based on multivariate correlation spectroscopy. Results demonstrated that the calibration correlation coefficient(R2C) and prediction correlation coefficient(R2p) for nicotine,benzoic acid,WS-23,propylene glycol,and glycerol all exceeded 0.98,indicating high accuracy in predicting these five additives. The cross-validation correlation coefficient(R2CV) for the WS-3 model was 0.95,suggesting potential for further optimization. The established quantitative models provide an effective tool for rapid quality assessment of E-liquids.关键词:near-infrared spectroscopy;e-liquids;additives;quantitative model;correlation coefficient395|76|0更新时间:2025-06-09
摘要:This study selected 160 commercially available and laboratory-prepared E-liquid samples for spectral scanning using a Fourier transform near-infrared(NIR) spectrometer(Thermo Fisher,USA). By comparing with chemical reference values,the near-infrared spectroscopy(NIRS) technique was validated for accurate prediction of six components in E-liquids:benzoic acid,nicotine,WS-23,WS-3,propylene glycol,and glycerol. Utilizing TQ Analyst software,partial least squares(PLS) regression was employed to establish quantitative models for these additives. Spectral preprocessing involved first-derivative transformation combined with Savitzky-Golay smoothing,and optimal wavelength ranges were determined based on multivariate correlation spectroscopy. Results demonstrated that the calibration correlation coefficient(R2C) and prediction correlation coefficient(R2p) for nicotine,benzoic acid,WS-23,propylene glycol,and glycerol all exceeded 0.98,indicating high accuracy in predicting these five additives. The cross-validation correlation coefficient(R2CV) for the WS-3 model was 0.95,suggesting potential for further optimization. The established quantitative models provide an effective tool for rapid quality assessment of E-liquids.关键词:near-infrared spectroscopy;e-liquids;additives;quantitative model;correlation coefficient395|76|0更新时间:2025-06-09 -
 摘要:An h multiple similarity index(HMSI) was proposed to evaluate batch consistency of traditional Chinese medicine fingerprints. HMSI was defined as follows:for the pairwise similarity of all objects in a batch(ranged from[0,1]),if M% of all the pairwise similarity values is not less than M%,then the value of HMSI is M%. Based on the high-performance liquid chromatography(HPLC) fingerprints of Radix Ophiopogon japonicus(Maidong) and Qingwei Huanglian Pills,the proposed HMSI was used to evaluate the quality consistency of different batches of Chinese herbal medicines,and the results were compared with those obtained by average similarity and median similarity. The results indicated that HMSI was suitable for HPLC fingerprints and was more reasonable to evaluate batch consistency than average similarity and median similarity. The index considers the similarity intensity of samples in a batch,as well as the number of samples with high similarity. HMSI is a simple,robust,easy-to-calculate and comprehensive index to evaluate batch consistency of traditional Chinese medicine fingerprints.关键词:traditional Chinese medicine;fingerprints;batch consistency;h multiple similarity index;similarity evaluation;high-performance liquid chromatography256|8|0更新时间:2025-06-09
摘要:An h multiple similarity index(HMSI) was proposed to evaluate batch consistency of traditional Chinese medicine fingerprints. HMSI was defined as follows:for the pairwise similarity of all objects in a batch(ranged from[0,1]),if M% of all the pairwise similarity values is not less than M%,then the value of HMSI is M%. Based on the high-performance liquid chromatography(HPLC) fingerprints of Radix Ophiopogon japonicus(Maidong) and Qingwei Huanglian Pills,the proposed HMSI was used to evaluate the quality consistency of different batches of Chinese herbal medicines,and the results were compared with those obtained by average similarity and median similarity. The results indicated that HMSI was suitable for HPLC fingerprints and was more reasonable to evaluate batch consistency than average similarity and median similarity. The index considers the similarity intensity of samples in a batch,as well as the number of samples with high similarity. HMSI is a simple,robust,easy-to-calculate and comprehensive index to evaluate batch consistency of traditional Chinese medicine fingerprints.关键词:traditional Chinese medicine;fingerprints;batch consistency;h multiple similarity index;similarity evaluation;high-performance liquid chromatography256|8|0更新时间:2025-06-09
Experimental Techniques and Methods
-
 摘要:Given the continuous evolution of criminal tactics,the field of forensic science urgently requires a technology capable of analyzing both the morphology and composition of physical evidence. Mass spectrometry imaging(MSI) technology,integrated with machine learning,offers a highly sensitive,specific,and extensive analysis method that is nearly non-destructive. It excels in the examination of fingerprints,documents,and physicochemical evidence by providing the potential to extract critical chemical information from rich datasets. This paper reviews the current state of research on MSI data analysis,including the tracing of the origin of residues,the analysis of the duration of residue presence,and image enhancement techniques. And this review highlights the integration of MSI with machine learning algorithms for the forensic analysis of various types of evidence. The synergy between MSI's ability to generate detailed chemical images and machine learning's data processing capabilities effectively addresses complex forensic challenges. The paper underscores the importance of this technology in enhancing the extraction of evidential information,thereby supporting more accurate and efficient investigations in legal proceedings. Despite the hurdles,such as operational complexity and the interpretability of algorithms,the future of forensic science,empowered by MSI and machine learning,appears poised to deliver transformative solutions to real-world forensic problems.关键词:mass spectrometry imaging;forensic science;machine learning;multivariate analysis209|10|0更新时间:2025-06-09
摘要:Given the continuous evolution of criminal tactics,the field of forensic science urgently requires a technology capable of analyzing both the morphology and composition of physical evidence. Mass spectrometry imaging(MSI) technology,integrated with machine learning,offers a highly sensitive,specific,and extensive analysis method that is nearly non-destructive. It excels in the examination of fingerprints,documents,and physicochemical evidence by providing the potential to extract critical chemical information from rich datasets. This paper reviews the current state of research on MSI data analysis,including the tracing of the origin of residues,the analysis of the duration of residue presence,and image enhancement techniques. And this review highlights the integration of MSI with machine learning algorithms for the forensic analysis of various types of evidence. The synergy between MSI's ability to generate detailed chemical images and machine learning's data processing capabilities effectively addresses complex forensic challenges. The paper underscores the importance of this technology in enhancing the extraction of evidential information,thereby supporting more accurate and efficient investigations in legal proceedings. Despite the hurdles,such as operational complexity and the interpretability of algorithms,the future of forensic science,empowered by MSI and machine learning,appears poised to deliver transformative solutions to real-world forensic problems.关键词:mass spectrometry imaging;forensic science;machine learning;multivariate analysis209|10|0更新时间:2025-06-09 -
 摘要:Plastic pollution stands as a significant environmental challenge of our time,with vast amounts of plastic waste entering aquatic environments through various pathways and degrading into microplastics(MPs) measuring less than 5 mm. These MPs are widely distributed in water bodies,posing a potential threat to ecosystems and human health. Thus,it is imperative to develop effective analytical methods for the identification and detection of MPs. Current MP identification techniques,including visual,spectroscopic,and chemical imaging methods,offer distinct advantages but are generally time-consuming,costly,and subject to human bias,thereby hindering technological advancement. The emerging chemometrics technology provides a powerful tool for processing and automating the analysis of large datasets,revolutionizing MP identification. Research has shown that combining traditional MPs recognition methods with chemometric techniques can increase recognition accuracy from 60% to 98%,and achieve automated data analysis,greatly improving efficiency and accuracy. In addition,the development of in-situ detection technology can help to reduce sampling costs and realize frequent and long-term monitoring of MPs. This review summarizes the existing methods for identifying MPs in aquatic environments along with their limitations,introduces the workflow of chemometrics,and discusses its current applications and latest developments in MP identification. It highlights the crucial role of chemometrics in data processing,technical optimization,and qualitative and quantitative analysis. Finally,the paper addresses some of the current limitations of chemometric technology and offers recommendations and perspectives for its further development and application.关键词:microplastics;aquatic ecosystem;chemometrics;identification243|53|0更新时间:2025-06-09
摘要:Plastic pollution stands as a significant environmental challenge of our time,with vast amounts of plastic waste entering aquatic environments through various pathways and degrading into microplastics(MPs) measuring less than 5 mm. These MPs are widely distributed in water bodies,posing a potential threat to ecosystems and human health. Thus,it is imperative to develop effective analytical methods for the identification and detection of MPs. Current MP identification techniques,including visual,spectroscopic,and chemical imaging methods,offer distinct advantages but are generally time-consuming,costly,and subject to human bias,thereby hindering technological advancement. The emerging chemometrics technology provides a powerful tool for processing and automating the analysis of large datasets,revolutionizing MP identification. Research has shown that combining traditional MPs recognition methods with chemometric techniques can increase recognition accuracy from 60% to 98%,and achieve automated data analysis,greatly improving efficiency and accuracy. In addition,the development of in-situ detection technology can help to reduce sampling costs and realize frequent and long-term monitoring of MPs. This review summarizes the existing methods for identifying MPs in aquatic environments along with their limitations,introduces the workflow of chemometrics,and discusses its current applications and latest developments in MP identification. It highlights the crucial role of chemometrics in data processing,technical optimization,and qualitative and quantitative analysis. Finally,the paper addresses some of the current limitations of chemometric technology and offers recommendations and perspectives for its further development and application.关键词:microplastics;aquatic ecosystem;chemometrics;identification243|53|0更新时间:2025-06-09 -
 摘要:With the deepening application of machine learning in spectral analysis,model training faces challenges such as data sample scarcity and class imbalance,which limit the model's generalization performance and lead to the risk of overfitting. This paper reviews the domestic and international literature published since 2017 and categorizes spectral data augmentation methods into two major types:non-deep learning data augmentation methods and deep learning data augmentation methods. It reveals the evolutionary trend from shallow data expansion to deep generative modeling. Non-deep learning data augmentation methods achieve data expansion through spectral transformation and spectral synthesis. Due to their computational efficiency,they show good applicability in small-sample scenarios such as industrial process monitoring,traditional Chinese medicine traceability,and drug and food quality detection. Deep generative models primarily include Generative Adversarial Networks(GAN) and their derivative methods,as well as improved Autoencoders(AE). GAN generates augmented samples with structural similarity and distribution consistency with the original data through adversarial game mechanisms. It is widely applied in high-precision modeling scenarios such as medical image diagnosis,precision agriculture,and materials classification. Improved AEs capture the intrinsic features of data through latent space representation learning,with generated data maintaining the original distribution characteristics while also having robust features. They have significant advantages in high-dimensional data processing tasks such as chemical substance identification and soil component detection. This review also highlights the limitations of existing data augmentation methods and discusses future development directions.关键词:Data augmentation;spectral analysis;deep learning;Generate adversarial network;Variational autoencoder217|93|0更新时间:2025-06-09
摘要:With the deepening application of machine learning in spectral analysis,model training faces challenges such as data sample scarcity and class imbalance,which limit the model's generalization performance and lead to the risk of overfitting. This paper reviews the domestic and international literature published since 2017 and categorizes spectral data augmentation methods into two major types:non-deep learning data augmentation methods and deep learning data augmentation methods. It reveals the evolutionary trend from shallow data expansion to deep generative modeling. Non-deep learning data augmentation methods achieve data expansion through spectral transformation and spectral synthesis. Due to their computational efficiency,they show good applicability in small-sample scenarios such as industrial process monitoring,traditional Chinese medicine traceability,and drug and food quality detection. Deep generative models primarily include Generative Adversarial Networks(GAN) and their derivative methods,as well as improved Autoencoders(AE). GAN generates augmented samples with structural similarity and distribution consistency with the original data through adversarial game mechanisms. It is widely applied in high-precision modeling scenarios such as medical image diagnosis,precision agriculture,and materials classification. Improved AEs capture the intrinsic features of data through latent space representation learning,with generated data maintaining the original distribution characteristics while also having robust features. They have significant advantages in high-dimensional data processing tasks such as chemical substance identification and soil component detection. This review also highlights the limitations of existing data augmentation methods and discusses future development directions.关键词:Data augmentation;spectral analysis;deep learning;Generate adversarial network;Variational autoencoder217|93|0更新时间:2025-06-09
Reviews
0

